Granger-causal Attentive Mixtures of Experts: Learning Important Features with Neural Networks
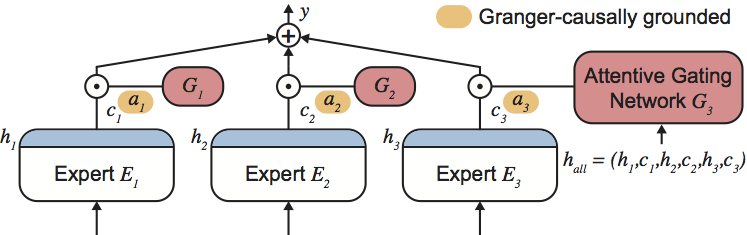
Knowledge of the importance of input features towards decisions made by machine-learning models is essential to increase our understanding of both the models and the underlying data. Here, we present a new approach to estimating feature importance with neural networks based on the idea of distributing the features of interest among experts in an attentive mixture of experts (AME). AMEs use attentive gating networks trained with a Granger-causal objective to learn to jointly produce accurate predictions as well as estimates of feature importance in a single model. Our experiments show (i) that the feature importance estimates provided by AMEs compare favourably to those provided by state-of-the-art methods, (ii) that AMEs are significantly faster at estimating feature importance than existing methods, and (iii) that the associations discovered by AMEs are consistent with those reported by domain experts.
PDF Abstract