Graph Neural Networks with Learnable Structural and Positional Representations
Graph neural networks (GNNs) have become the standard learning architectures for graphs. GNNs have been applied to numerous domains ranging from quantum chemistry, recommender systems to knowledge graphs and natural language processing. A major issue with arbitrary graphs is the absence of canonical positional information of nodes, which decreases the representation power of GNNs to distinguish e.g. isomorphic nodes and other graph symmetries. An approach to tackle this issue is to introduce Positional Encoding (PE) of nodes, and inject it into the input layer, like in Transformers. Possible graph PE are Laplacian eigenvectors. In this work, we propose to decouple structural and positional representations to make easy for the network to learn these two essential properties. We introduce a novel generic architecture which we call LSPE (Learnable Structural and Positional Encodings). We investigate several sparse and fully-connected (Transformer-like) GNNs, and observe a performance increase for molecular datasets, from 1.79% up to 64.14% when considering learnable PE for both GNN classes.
PDF Abstract ICLR 2022 PDF ICLR 2022 Abstract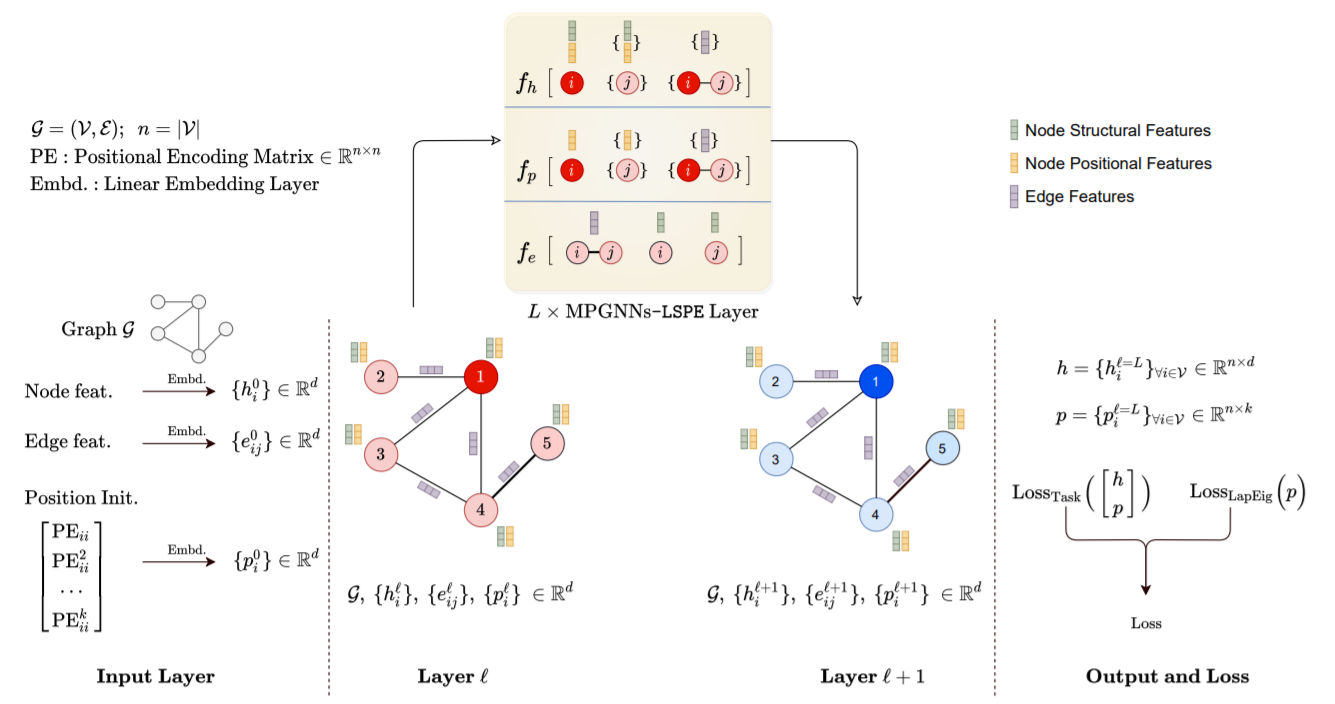




 OGB
OGB
 ZINC
ZINC
