HaluEval: A Large-Scale Hallucination Evaluation Benchmark for Large Language Models
Large language models (LLMs), such as ChatGPT, are prone to generate hallucinations, i.e., content that conflicts with the source or cannot be verified by the factual knowledge. To understand what types of content and to which extent LLMs are apt to hallucinate, we introduce the Hallucination Evaluation benchmark for Large Language Models (HaluEval), a large collection of generated and human-annotated hallucinated samples for evaluating the performance of LLMs in recognizing hallucination. To generate these samples, we propose a ChatGPT-based two-step framework, i.e., sampling-then-filtering. Besides, we also hire some human labelers to annotate the hallucinations in ChatGPT responses. The empirical results suggest that ChatGPT is likely to generate hallucinated content in specific topics by fabricating unverifiable information (i.e., about $19.5\%$ responses). Moreover, existing LLMs face great challenges in recognizing the hallucinations in texts. However, our experiments also prove that providing external knowledge or adding reasoning steps can help LLMs recognize hallucinations. Our benchmark can be accessed at https://github.com/RUCAIBox/HaluEval.
PDF Abstract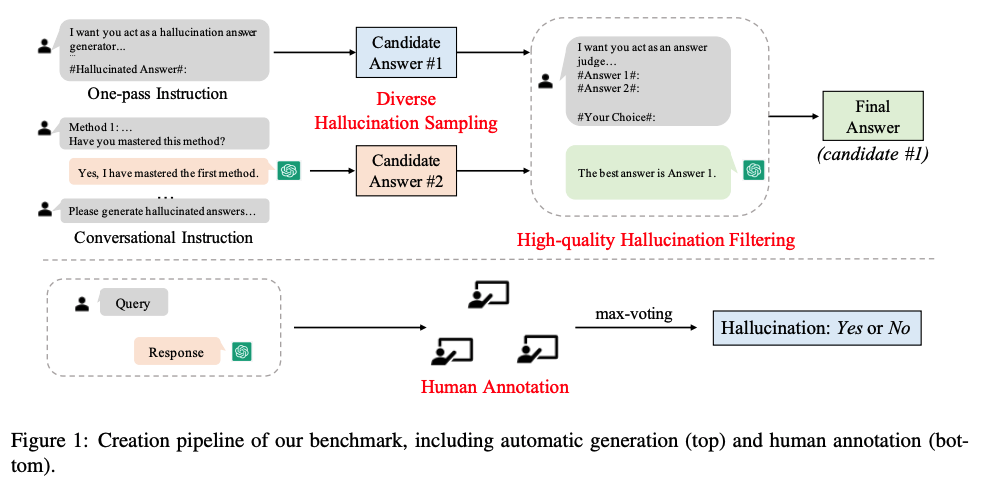

 HotpotQA
HotpotQA