HIDA: Towards Holistic Indoor Understanding for the Visually Impaired via Semantic Instance Segmentation with a Wearable Solid-State LiDAR Sensor
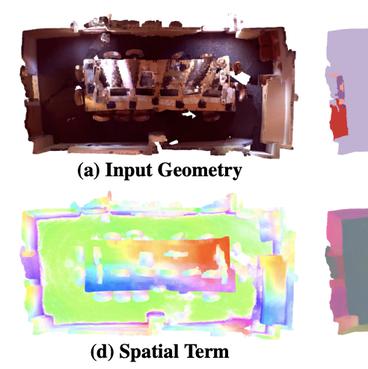
Independently exploring unknown spaces or finding objects in an indoor environment is a daily but challenging task for visually impaired people. However, common 2D assistive systems lack depth relationships between various objects, resulting in difficulty to obtain accurate spatial layout and relative positions of objects. To tackle these issues, we propose HIDA, a lightweight assistive system based on 3D point cloud instance segmentation with a solid-state LiDAR sensor, for holistic indoor detection and avoidance. Our entire system consists of three hardware components, two interactive functions~(obstacle avoidance and object finding) and a voice user interface. Based on voice guidance, the point cloud from the most recent state of the changing indoor environment is captured through an on-site scanning performed by the user. In addition, we design a point cloud segmentation model with dual lightweight decoders for semantic and offset predictions, which satisfies the efficiency of the whole system. After the 3D instance segmentation, we post-process the segmented point cloud by removing outliers and projecting all points onto a top-view 2D map representation. The system integrates the information above and interacts with users intuitively by acoustic feedback. The proposed 3D instance segmentation model has achieved state-of-the-art performance on ScanNet v2 dataset. Comprehensive field tests with various tasks in a user study verify the usability and effectiveness of our system for assisting visually impaired people in holistic indoor understanding, obstacle avoidance and object search.
PDF Abstract




 ScanNet
ScanNet
