Hijacking Malaria Simulators with Probabilistic Programming
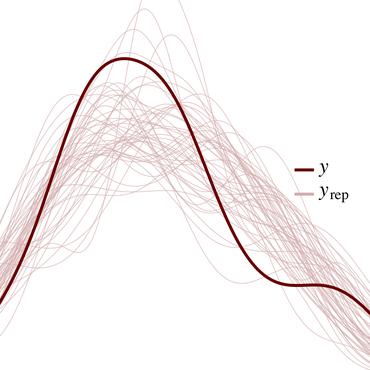
Epidemiology simulations have become a fundamental tool in the fight against the epidemics of various infectious diseases like AIDS and malaria. However, the complicated and stochastic nature of these simulators can mean their output is difficult to interpret, which reduces their usefulness to policymakers. In this paper, we introduce an approach that allows one to treat a large class of population-based epidemiology simulators as probabilistic generative models. This is achieved by hijacking the internal random number generator calls, through the use of a universal probabilistic programming system (PPS). In contrast to other methods, our approach can be easily retrofitted to simulators written in popular industrial programming frameworks. We demonstrate that our method can be used for interpretable introspection and inference, thus shedding light on black-box simulators. This reinstates much-needed trust between policymakers and evidence-based methods.
PDF Abstract