Improving Point Cloud Based Place Recognition with Ranking-based Loss and Large Batch Training
The paper presents a simple and effective learning-based method for computing a discriminative 3D point cloud descriptor for place recognition purposes. Recent state-of-the-art methods have relatively complex architectures such as multi-scale oyramid of point Transformers combined with a pyramid of feature aggregation modules. Our method uses a simple and efficient 3D convolutional feature extraction, based on a sparse voxelized representation, enhanced with channel attention blocks. We employ recent advances in image retrieval and propose a modified version of a loss function based on a differentiable average precision approximation. Such loss function requires training with very large batches for the best results. This is enabled by using multistaged backpropagation. Experimental evaluation on the popular benchmarks proves the effectiveness of our approach, with a consistent improvement over the state of the art
PDF Abstract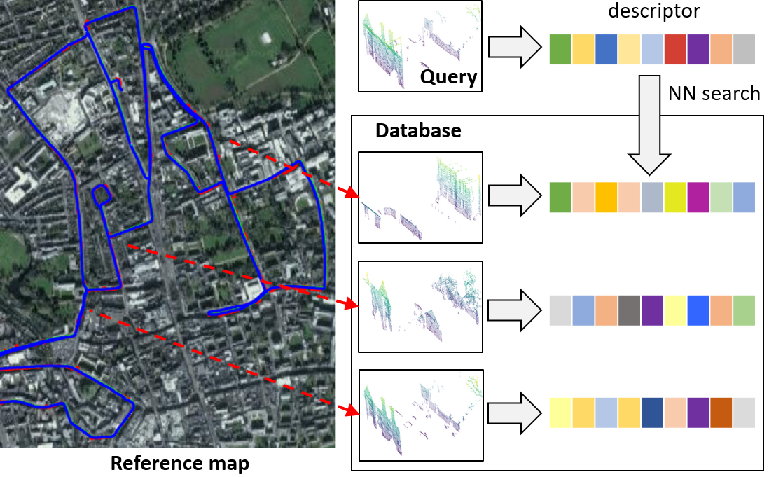






 Oxford RobotCar Dataset
Oxford RobotCar Dataset
