Instance Adaptive Self-Training for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
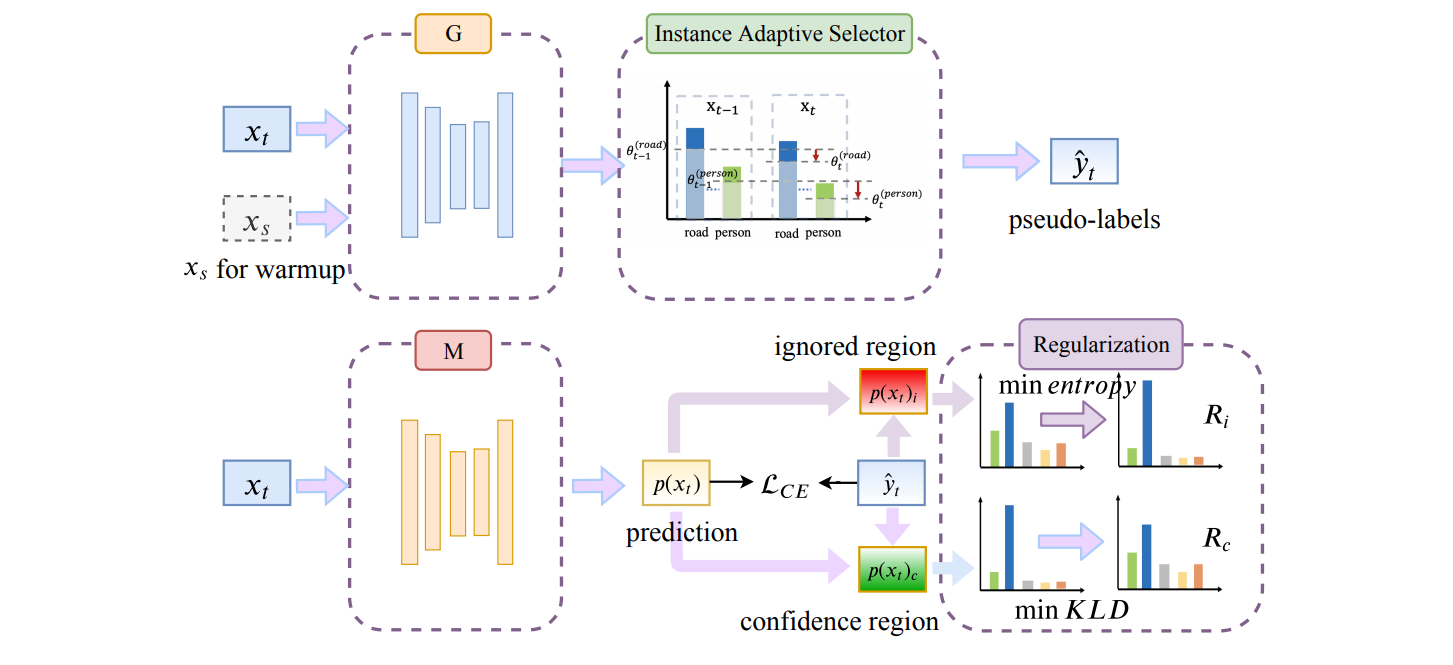
The divergence between labeled training data and unlabeled testing data is a significant challenge for recent deep learning models. Unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) attempts to solve such a problem. Recent works show that self-training is a powerful approach to UDA. However, existing methods have difficulty in balancing scalability and performance. In this paper, we propose an instance adaptive self-training framework for UDA on the task of semantic segmentation. To effectively improve the quality of pseudo-labels, we develop a novel pseudo-label generation strategy with an instance adaptive selector. Besides, we propose the region-guided regularization to smooth the pseudo-label region and sharpen the non-pseudo-label region. Our method is so concise and efficient that it is easy to be generalized to other unsupervised domain adaptation methods. Experiments on 'GTA5 to Cityscapes' and 'SYNTHIA to Cityscapes' demonstrate the superior performance of our approach compared with the state-of-the-art methods.
PDF Abstract ECCV 2020 PDF ECCV 2020 AbstractCode
Datasets
Results from the Paper
| Task | Dataset | Model | Metric Name | Metric Value | Global Rank | Benchmark |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synthetic-to-Real Translation | GTAV-to-Cityscapes Labels | IAST | mIoU | 51.5 | # 40 | |
| Image-to-Image Translation | SYNTHIA-to-Cityscapes | IAST(ResNet-101) | mIoU (13 classes) | 57.0 | # 13 | |
| Domain Adaptation | SYNTHIA-to-Cityscapes | IAST (ResNet-101) | mIoU | 49.8 | # 18 | |
| Synthetic-to-Real Translation | SYNTHIA-to-Cityscapes | IAST(ResNet-101) | MIoU (13 classes) | 57.0 | # 21 | |
| MIoU (16 classes) | 49.8 | # 20 |










 Cityscapes
Cityscapes
 SYNTHIA
SYNTHIA
 GTA5
GTA5
