Integrated monitoring of ice in selected Swiss lakes. Final project report
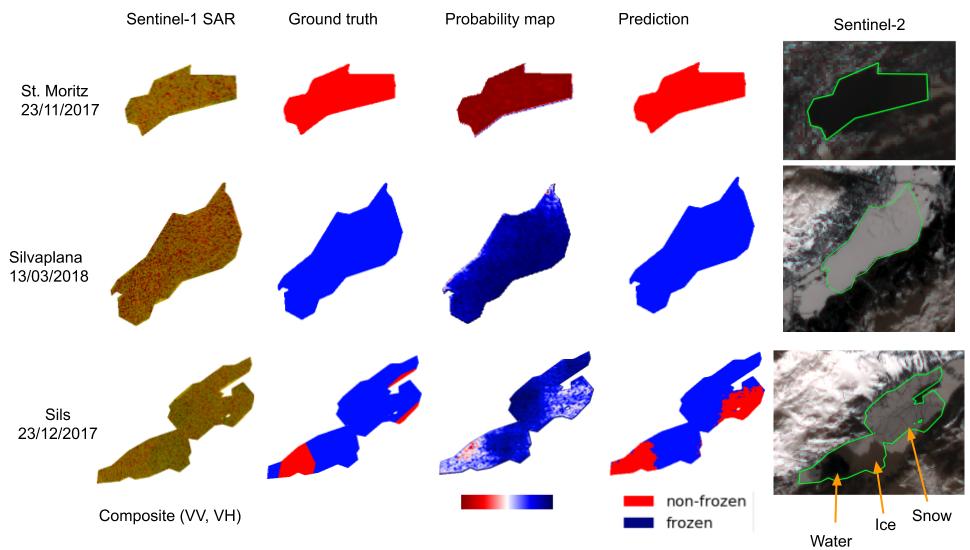
Various lake observables, including lake ice, are related to climate and climate change and provide a good opportunity for long-term monitoring. Lakes (and as part of them lake ice) is therefore considered an Essential Climate Variable (ECV) of the Global Climate Observing System (GCOS). Following the need for an integrated multi-temporal monitoring of lake ice in Switzerland, MeteoSwiss in the framework of GCOS Switzerland supported this 2-year project to explore not only the use of satellite images but also the possibilities of Webcams and in-situ measurements. The aim of this project is to monitor some target lakes and detect the extent of ice and especially the ice-on/off dates, with focus on the integration of various input data and processing methods. The target lakes are: St. Moritz, Silvaplana, Sils, Sihl, Greifen and Aegeri, whereby only the first four were mainly frozen during the observation period and thus processed. The observation period was mainly the winter 2016-17. During the project, various approaches were developed, implemented, tested and compared. Firstly, low spatial resolution (250 - 1000 m) but high temporal resolution (1 day) satellite images from the optical sensors MODIS and VIIRS were used. Secondly, and as a pilot project, the use of existing public Webcams was investigated for (a) validation of results from satellite data, and (b) independent estimation of lake ice, especially for small lakes like St. Moritz, that could not be possibly monitored in the satellite images. Thirdly, in-situ measurements were made in order to characterize the development of the temperature profiles and partly pressure before freezing and under the ice-cover until melting. This report presents the results of the project work.
PDF Abstract