BINAS: Bilinear Interpretable Neural Architecture Search
Practical use of neural networks often involves requirements on latency, energy and memory among others. A popular approach to find networks under such requirements is through constrained Neural Architecture Search (NAS). However, previous methods use complicated predictors for the accuracy of the network. Those predictors are hard to interpret and sensitive to many hyperparameters to be tuned, hence, the resulting accuracy of the generated models is often harmed. In this work we resolve this by introducing Bilinear Interpretable Neural Architecture Search (BINAS), that is based on an accurate and simple bilinear formulation of both an accuracy estimator and the expected resource requirement, together with a scalable search method with theoretical guarantees. The simplicity of our proposed estimator together with the intuitive way it is constructed bring interpretability through many insights about the contribution of different design choices. For example, we find that in the examined search space, adding depth and width is more effective at deeper stages of the network and at the beginning of each resolution stage. Our experiments show that BINAS generates comparable to or better architectures than other state-of-the-art NAS methods within a reduced marginal search cost, while strictly satisfying the resource constraints.
PDF Abstract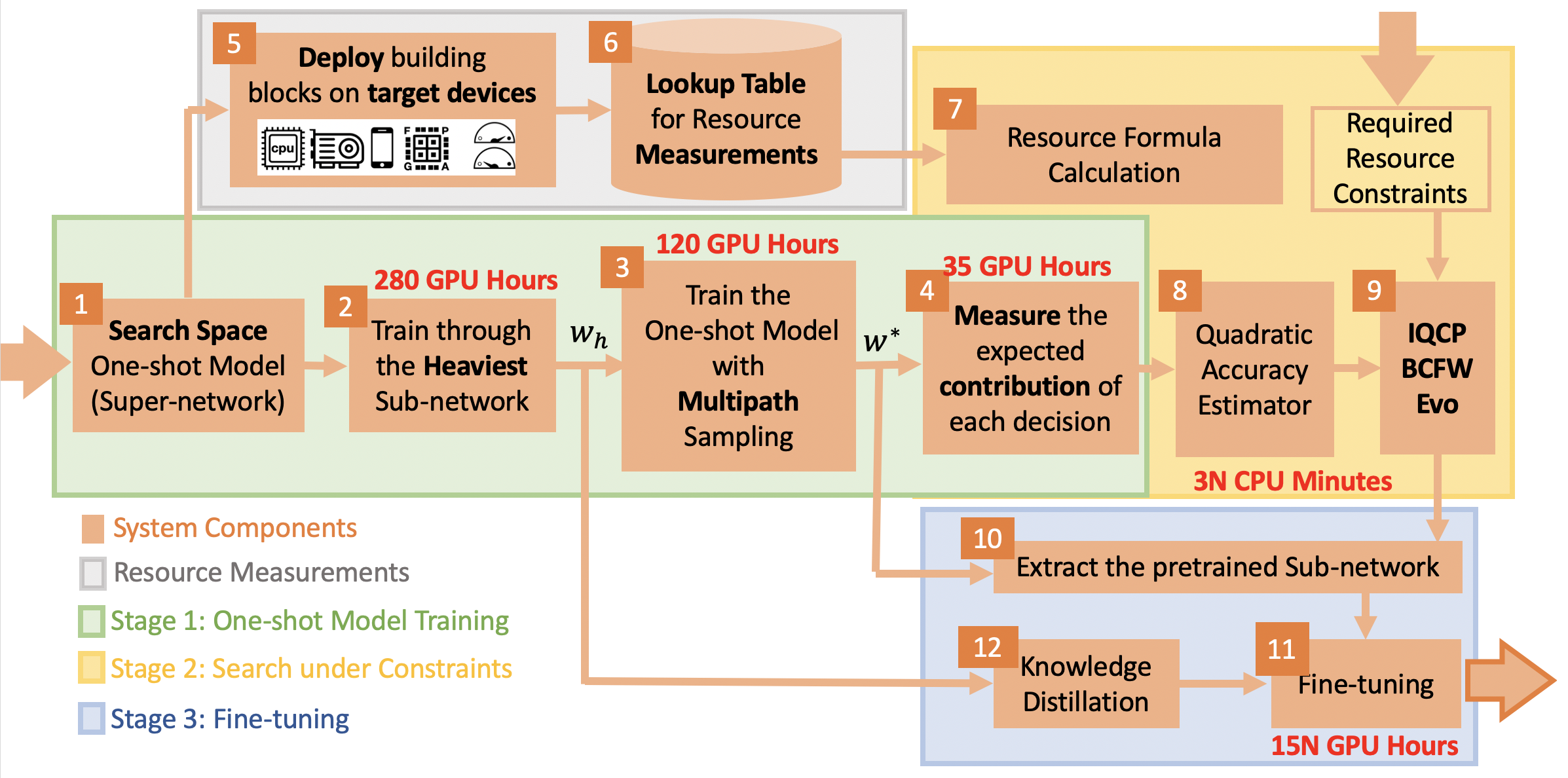


 ImageNet
ImageNet