Label-Noise Robust Generative Adversarial Networks
Generative adversarial networks (GANs) are a framework that learns a generative distribution through adversarial training. Recently, their class-conditional extensions (e.g., conditional GAN (cGAN) and auxiliary classifier GAN (AC-GAN)) have attracted much attention owing to their ability to learn the disentangled representations and to improve the training stability. However, their training requires the availability of large-scale accurate class-labeled data, which are often laborious or impractical to collect in a real-world scenario. To remedy this, we propose a novel family of GANs called label-noise robust GANs (rGANs), which, by incorporating a noise transition model, can learn a clean label conditional generative distribution even when training labels are noisy. In particular, we propose two variants: rAC-GAN, which is a bridging model between AC-GAN and the label-noise robust classification model, and rcGAN, which is an extension of cGAN and solves this problem with no reliance on any classifier. In addition to providing the theoretical background, we demonstrate the effectiveness of our models through extensive experiments using diverse GAN configurations, various noise settings, and multiple evaluation metrics (in which we tested 402 conditions in total). Our code is available at https://github.com/takuhirok/rGAN/.
PDF Abstract CVPR 2019 PDF CVPR 2019 Abstract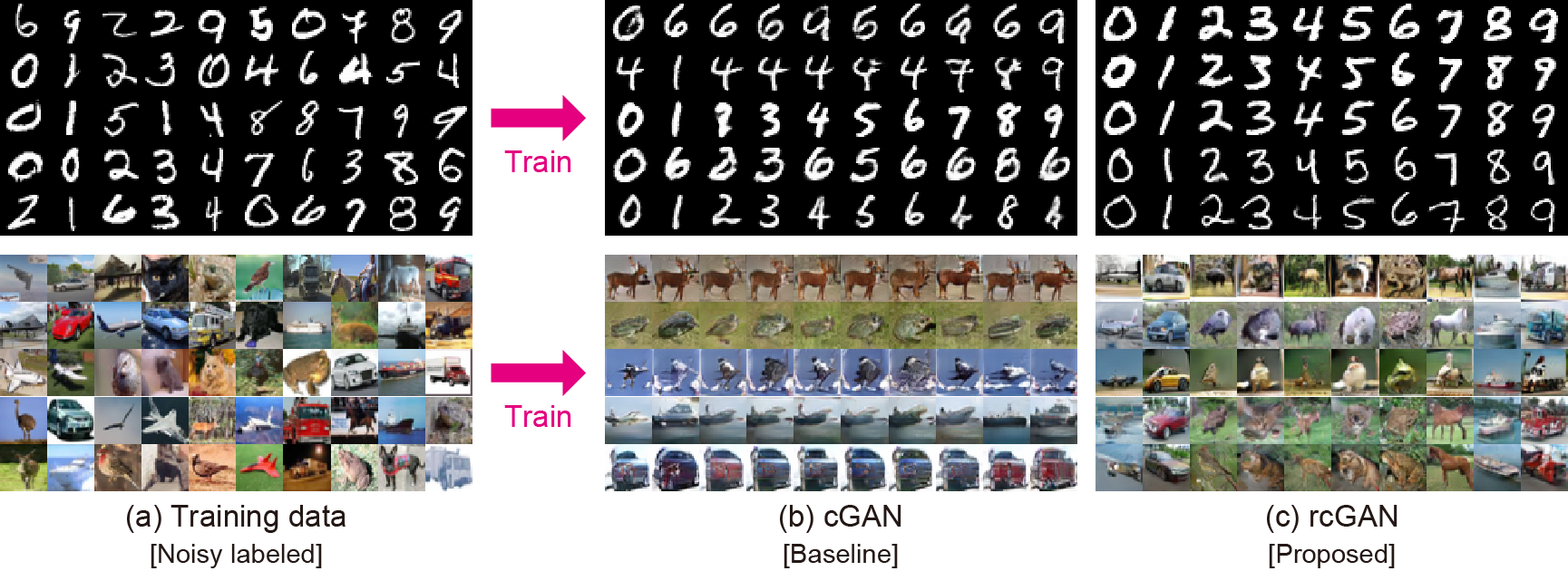


 Clothing1M
Clothing1M