LambdaNetworks: Modeling Long-Range Interactions Without Attention
We present lambda layers -- an alternative framework to self-attention -- for capturing long-range interactions between an input and structured contextual information (e.g. a pixel surrounded by other pixels). Lambda layers capture such interactions by transforming available contexts into linear functions, termed lambdas, and applying these linear functions to each input separately. Similar to linear attention, lambda layers bypass expensive attention maps, but in contrast, they model both content and position-based interactions which enables their application to large structured inputs such as images. The resulting neural network architectures, LambdaNetworks, significantly outperform their convolutional and attentional counterparts on ImageNet classification, COCO object detection and COCO instance segmentation, while being more computationally efficient. Additionally, we design LambdaResNets, a family of hybrid architectures across different scales, that considerably improves the speed-accuracy tradeoff of image classification models. LambdaResNets reach excellent accuracies on ImageNet while being 3.2 - 4.4x faster than the popular EfficientNets on modern machine learning accelerators. When training with an additional 130M pseudo-labeled images, LambdaResNets achieve up to a 9.5x speed-up over the corresponding EfficientNet checkpoints.
PDF Abstract ICLR 2021 PDF ICLR 2021 Abstract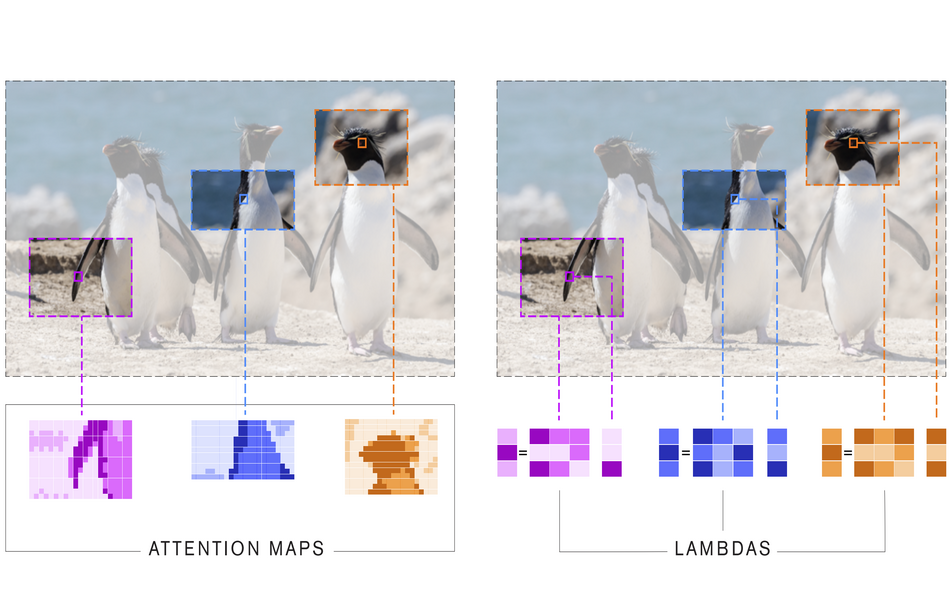







 ImageNet
ImageNet
 MS COCO
MS COCO
