Learning from Synthetic Animals
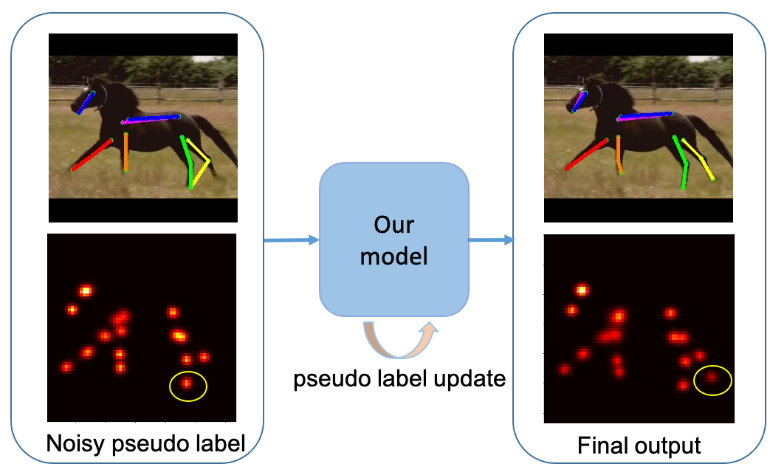
Despite great success in human parsing, progress for parsing other deformable articulated objects, like animals, is still limited by the lack of labeled data. In this paper, we use synthetic images and ground truth generated from CAD animal models to address this challenge. To bridge the domain gap between real and synthetic images, we propose a novel consistency-constrained semi-supervised learning method (CC-SSL). Our method leverages both spatial and temporal consistencies, to bootstrap weak models trained on synthetic data with unlabeled real images. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our method on highly deformable animals, such as horses and tigers. Without using any real image label, our method allows for accurate keypoint prediction on real images. Moreover, we quantitatively show that models using synthetic data achieve better generalization performance than models trained on real images across different domains in the Visual Domain Adaptation Challenge dataset. Our synthetic dataset contains 10+ animals with diverse poses and rich ground truth, which enables us to use the multi-task learning strategy to further boost models' performance.
PDF Abstract CVPR 2020 PDF CVPR 2020 Abstract