Learning Similarity Conditions Without Explicit Supervision
Many real-world tasks require models to compare images along multiple similarity conditions (e.g. similarity in color, category or shape). Existing methods often reason about these complex similarity relationships by learning condition-aware embeddings. While such embeddings aid models in learning different notions of similarity, they also limit their capability to generalize to unseen categories since they require explicit labels at test time. To address this deficiency, we propose an approach that jointly learns representations for the different similarity conditions and their contributions as a latent variable without explicit supervision. Comprehensive experiments across three datasets, Polyvore-Outfits, Maryland-Polyvore and UT-Zappos50k, demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach: our model outperforms the state-of-the-art methods, even those that are strongly supervised with pre-defined similarity conditions, on fill-in-the-blank, outfit compatibility prediction and triplet prediction tasks. Finally, we show that our model learns different visually-relevant semantic sub-spaces that allow it to generalize well to unseen categories.
PDF Abstract ICCV 2019 PDF ICCV 2019 Abstract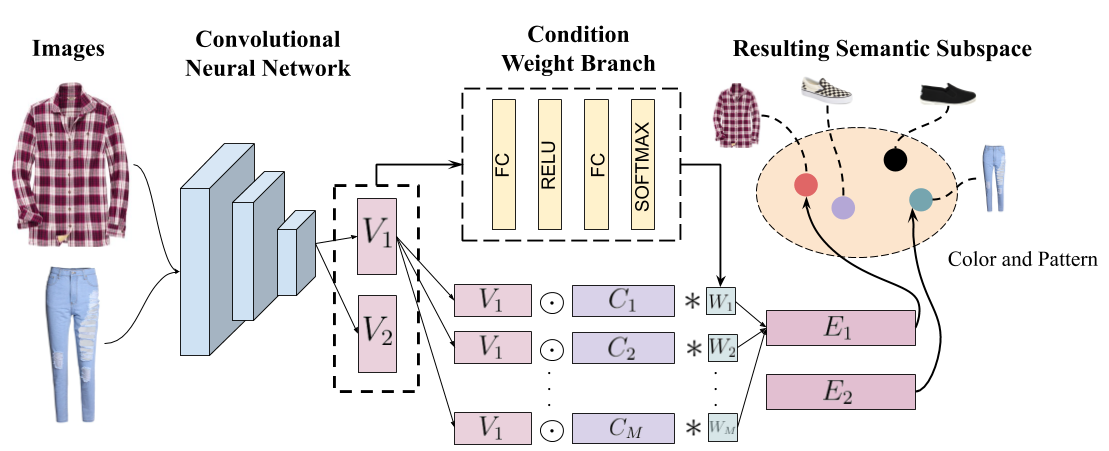

 Polyvore
Polyvore