Learning Transferable Adversarial Examples via Ghost Networks
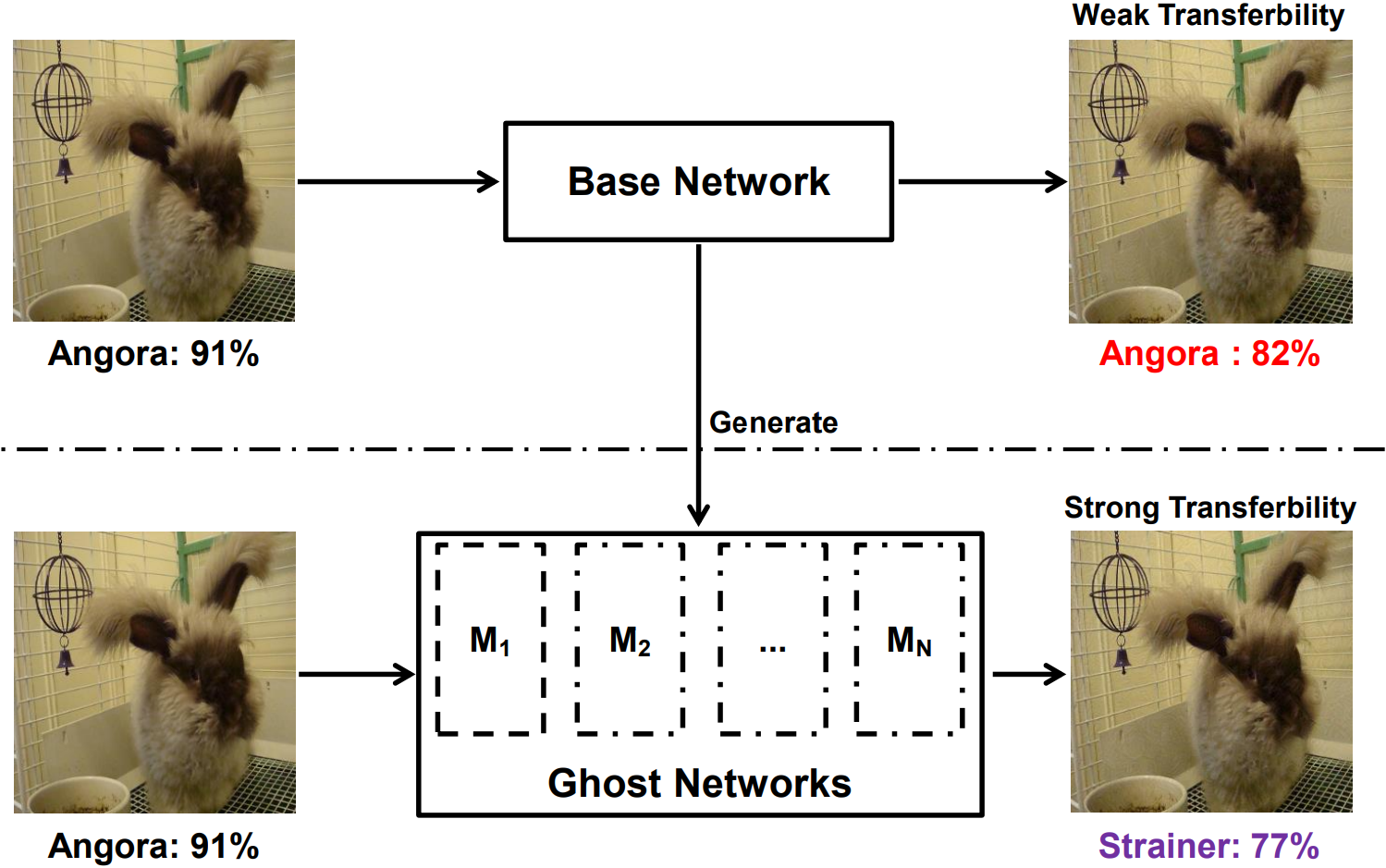
Recent development of adversarial attacks has proven that ensemble-based methods outperform traditional, non-ensemble ones in black-box attack. However, as it is computationally prohibitive to acquire a family of diverse models, these methods achieve inferior performance constrained by the limited number of models to be ensembled. In this paper, we propose Ghost Networks to improve the transferability of adversarial examples. The critical principle of ghost networks is to apply feature-level perturbations to an existing model to potentially create a huge set of diverse models. After that, models are subsequently fused by longitudinal ensemble. Extensive experimental results suggest that the number of networks is essential for improving the transferability of adversarial examples, but it is less necessary to independently train different networks and ensemble them in an intensive aggregation way. Instead, our work can be used as a computationally cheap and easily applied plug-in to improve adversarial approaches both in single-model and multi-model attack, compatible with residual and non-residual networks. By reproducing the NeurIPS 2017 adversarial competition, our method outperforms the No.1 attack submission by a large margin, demonstrating its effectiveness and efficiency. Code is available at https://github.com/LiYingwei/ghost-network.
PDF Abstract