Learning Vector-Quantized Item Representation for Transferable Sequential Recommenders
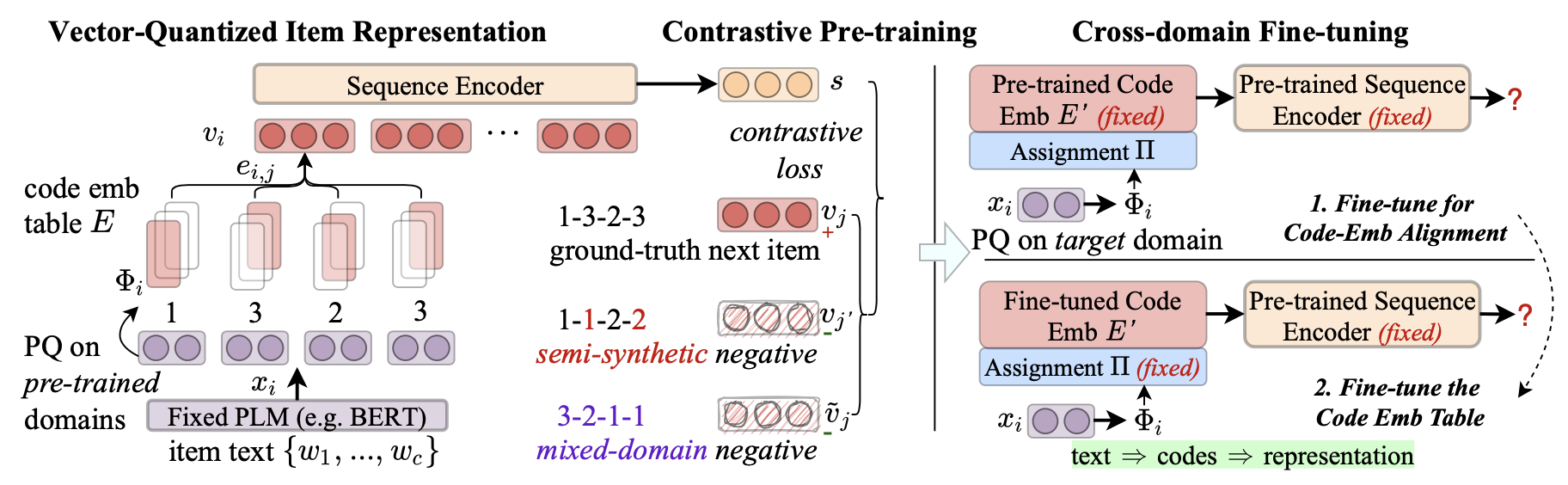
Recently, the generality of natural language text has been leveraged to develop transferable recommender systems. The basic idea is to employ pre-trained language models~(PLM) to encode item text into item representations. Despite the promising transferability, the binding between item text and item representations might be too tight, leading to potential problems such as over-emphasizing the effect of text features and exaggerating the negative impact of domain gap. To address this issue, this paper proposes VQ-Rec, a novel approach to learning Vector-Quantized item representations for transferable sequential Recommenders. The main novelty of our approach lies in the new item representation scheme: it first maps item text into a vector of discrete indices (called item code), and then employs these indices to lookup the code embedding table for deriving item representations. Such a scheme can be denoted as "text $\Longrightarrow$ code $\Longrightarrow$ representation". Based on this representation scheme, we further propose an enhanced contrastive pre-training approach, using semi-synthetic and mixed-domain code representations as hard negatives. Furthermore, we design a new cross-domain fine-tuning method based on a differentiable permutation-based network. Extensive experiments conducted on six public benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach, in both cross-domain and cross-platform settings. Code and pre-trained model are available at: https://github.com/RUCAIBox/VQ-Rec.
PDF Abstract