Lipophilicity Prediction with Multitask Learning and Molecular Substructures Representation
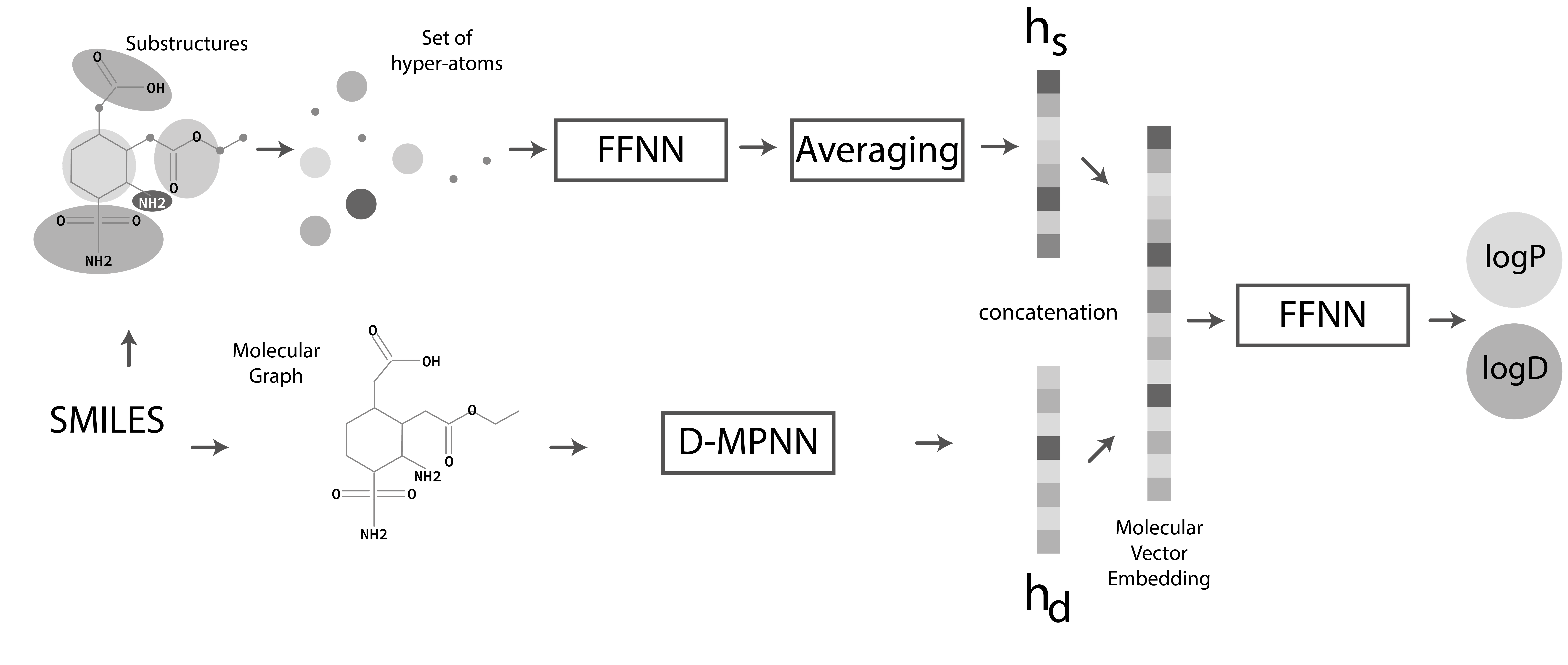
Lipophilicity is one of the factors determining the permeability of the cell membrane to a drug molecule. Hence, accurate lipophilicity prediction is an essential step in the development of new drugs. In this paper, we introduce a novel approach to encoding additional graph information by extracting molecular substructures. By adding a set of generalized atomic features of these substructures to an established Direct Message Passing Neural Network (D-MPNN) we were able to achieve a new state-of-the-art result at the task of prediction of two main lipophilicity coefficients, namely logP and logD descriptors. We further improve our approach by employing a multitask approach to predict logP and logD values simultaneously. Additionally, we present a study of the model performance on symmetric and asymmetric molecules, that may yield insight for further research.
PDF Abstract