Logical Learning Through a Hybrid Neural Network with Auxiliary Inputs
The human reasoning process is seldom a one-way process from an input leading to an output. Instead, it often involves a systematic deduction by ruling out other possible outcomes as a self-checking mechanism. In this paper, we describe the design of a hybrid neural network for logical learning that is similar to the human reasoning through the introduction of an auxiliary input, namely the indicators, that act as the hints to suggest logical outcomes. We generate these indicators by digging into the hidden information buried underneath the original training data for direct or indirect suggestions. We used the MNIST data to demonstrate the design and use of these indicators in a convolutional neural network. We trained a series of such hybrid neural networks with variations of the indicators. Our results show that these hybrid neural networks are very robust in generating logical outcomes with inherently higher prediction accuracy than the direct use of the original input and output in apparent models. Such improved predictability with reassured logical confidence is obtained through the exhaustion of all possible indicators to rule out all illogical outcomes, which is not available in the apparent models. Our logical learning process can effectively cope with the unknown unknowns using a full exploitation of all existing knowledge available for learning. The design and implementation of the hints, namely the indicators, become an essential part of artificial intelligence for logical learning. We also introduce an ongoing application setup for this hybrid neural network in an autonomous grasping robot, namely as_DeepClaw, aiming at learning an optimized grasping pose through logical learning.
PDF Abstract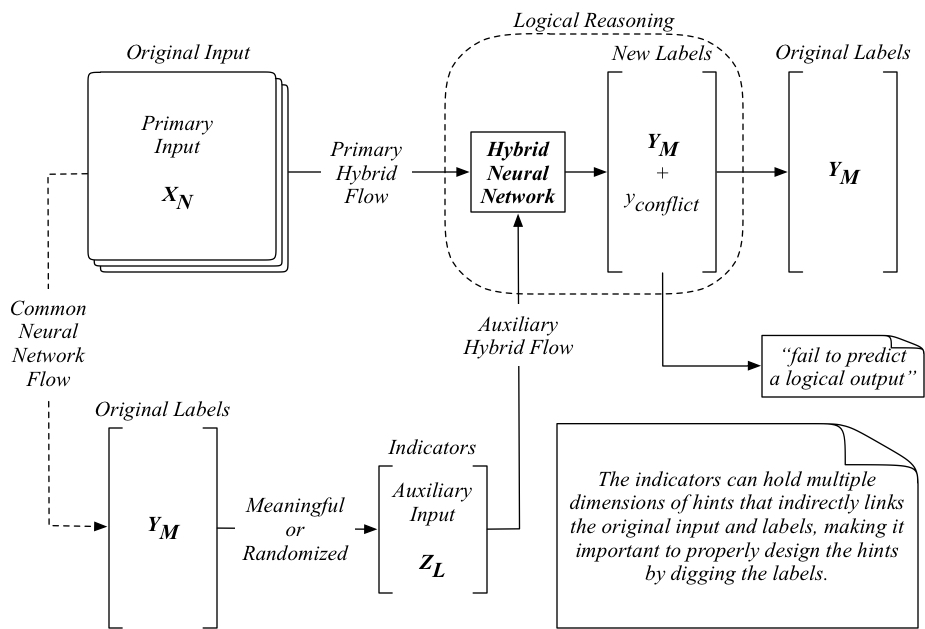
 MNIST
MNIST