LoST? Appearance-Invariant Place Recognition for Opposite Viewpoints using Visual Semantics
Human visual scene understanding is so remarkable that we are able to recognize a revisited place when entering it from the opposite direction it was first visited, even in the presence of extreme variations in appearance. This capability is especially apparent during driving: a human driver can recognize where they are when travelling in the reverse direction along a route for the first time, without having to turn back and look. The difficulty of this problem exceeds any addressed in past appearance- and viewpoint-invariant visual place recognition (VPR) research, in part because large parts of the scene are not commonly observable from opposite directions. Consequently, as shown in this paper, the precision-recall performance of current state-of-the-art viewpoint- and appearance-invariant VPR techniques is orders of magnitude below what would be usable in a closed-loop system. Current engineered solutions predominantly rely on panoramic camera or LIDAR sensing setups; an eminently suitable engineering solution but one that is clearly very different to how humans navigate, which also has implications for how naturally humans could interact and communicate with the navigation system. In this paper we develop a suite of novel semantic- and appearance-based techniques to enable for the first time high performance place recognition in this challenging scenario. We first propose a novel Local Semantic Tensor (LoST) descriptor of images using the convolutional feature maps from a state-of-the-art dense semantic segmentation network. Then, to verify the spatial semantic arrangement of the top matching candidates, we develop a novel approach for mining semantically-salient keypoint correspondences.
PDF Abstract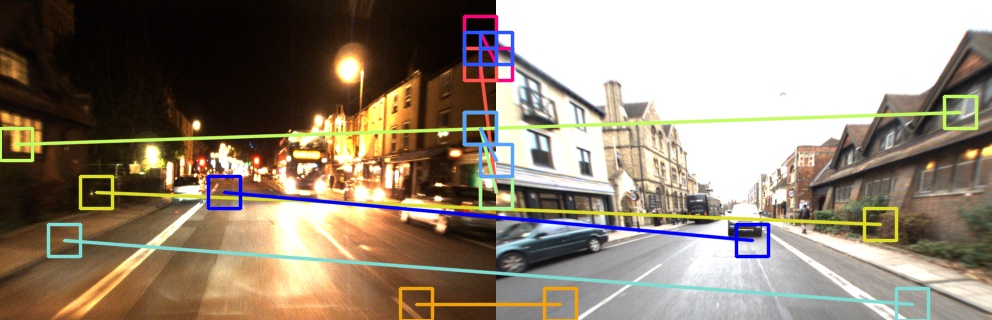



 Cityscapes
Cityscapes
 Places
Places
 SYNTHIA
SYNTHIA