Masked Autoencoders that Listen
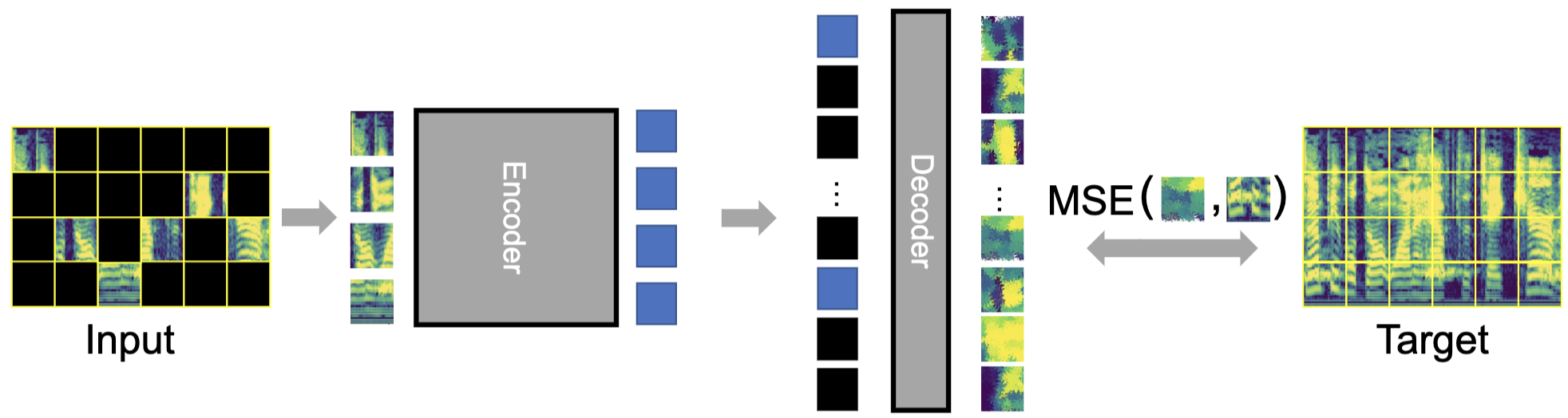
This paper studies a simple extension of image-based Masked Autoencoders (MAE) to self-supervised representation learning from audio spectrograms. Following the Transformer encoder-decoder design in MAE, our Audio-MAE first encodes audio spectrogram patches with a high masking ratio, feeding only the non-masked tokens through encoder layers. The decoder then re-orders and decodes the encoded context padded with mask tokens, in order to reconstruct the input spectrogram. We find it beneficial to incorporate local window attention in the decoder, as audio spectrograms are highly correlated in local time and frequency bands. We then fine-tune the encoder with a lower masking ratio on target datasets. Empirically, Audio-MAE sets new state-of-the-art performance on six audio and speech classification tasks, outperforming other recent models that use external supervised pre-training. The code and models will be at https://github.com/facebookresearch/AudioMAE.
PDF AbstractCode
Datasets
Results from the Paper
 Ranked #2 on
Speaker Identification
on VoxCeleb1
(using extra training data)
Ranked #2 on
Speaker Identification
on VoxCeleb1
(using extra training data)





 VoxCeleb1
VoxCeleb1
 AudioSet
AudioSet
 Speech Commands
Speech Commands
 ESC-50
ESC-50