Mitigating Covariate Shift in Imitation Learning via Offline Data Without Great Coverage
This paper studies offline Imitation Learning (IL) where an agent learns to imitate an expert demonstrator without additional online environment interactions. Instead, the learner is presented with a static offline dataset of state-action-next state transition triples from a potentially less proficient behavior policy. We introduce Model-based IL from Offline data (MILO): an algorithmic framework that utilizes the static dataset to solve the offline IL problem efficiently both in theory and in practice. In theory, even if the behavior policy is highly sub-optimal compared to the expert, we show that as long as the data from the behavior policy provides sufficient coverage on the expert state-action traces (and with no necessity for a global coverage over the entire state-action space), MILO can provably combat the covariate shift issue in IL. Complementing our theory results, we also demonstrate that a practical implementation of our approach mitigates covariate shift on benchmark MuJoCo continuous control tasks. We demonstrate that with behavior policies whose performances are less than half of that of the expert, MILO still successfully imitates with an extremely low number of expert state-action pairs while traditional offline IL method such as behavior cloning (BC) fails completely. Source code is provided at https://github.com/jdchang1/milo.
PDF Abstract NeurIPS 2021 PDF NeurIPS 2021 Abstract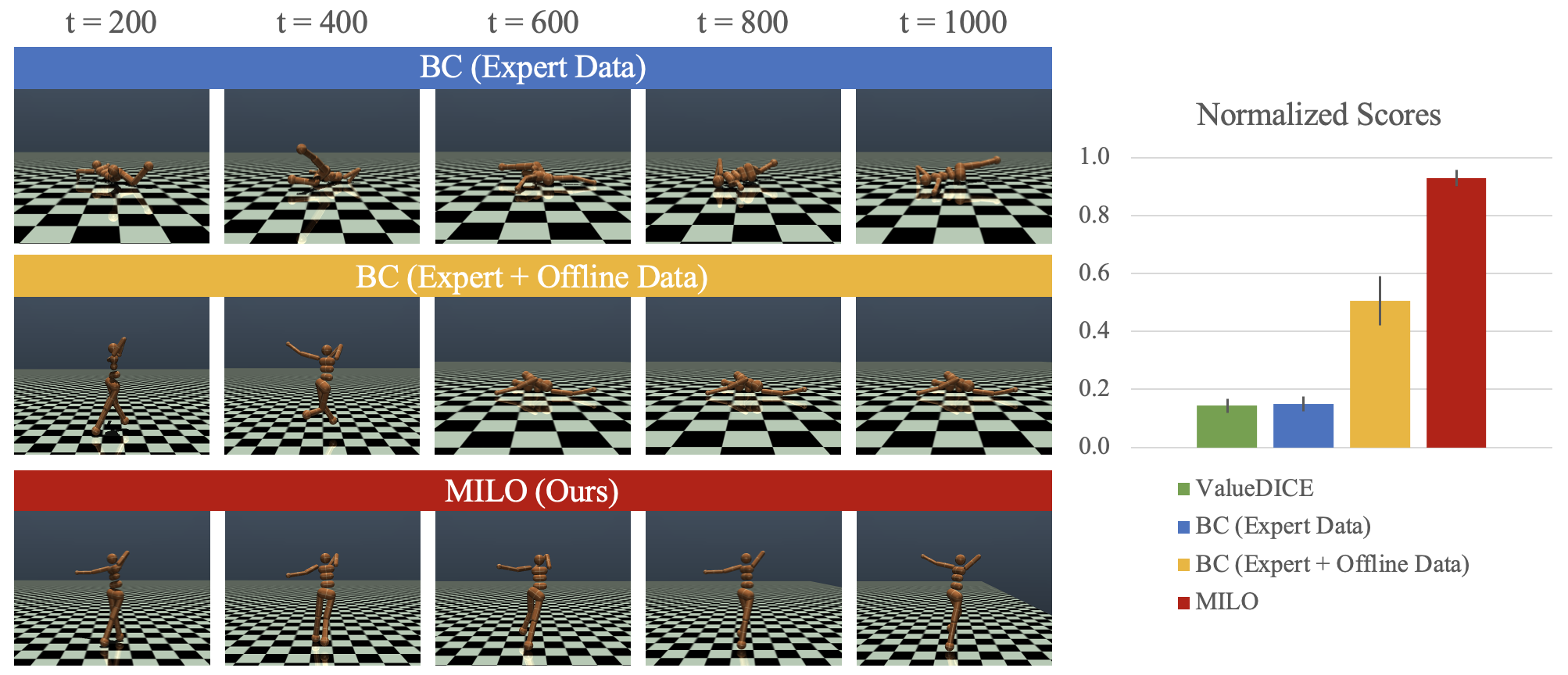


 MuJoCo
MuJoCo