Model-based Synthetic Data-driven Learning (MOST-DL): Application in Single-shot T2 Mapping with Severe Head Motion Using Overlapping-echo Acquisition
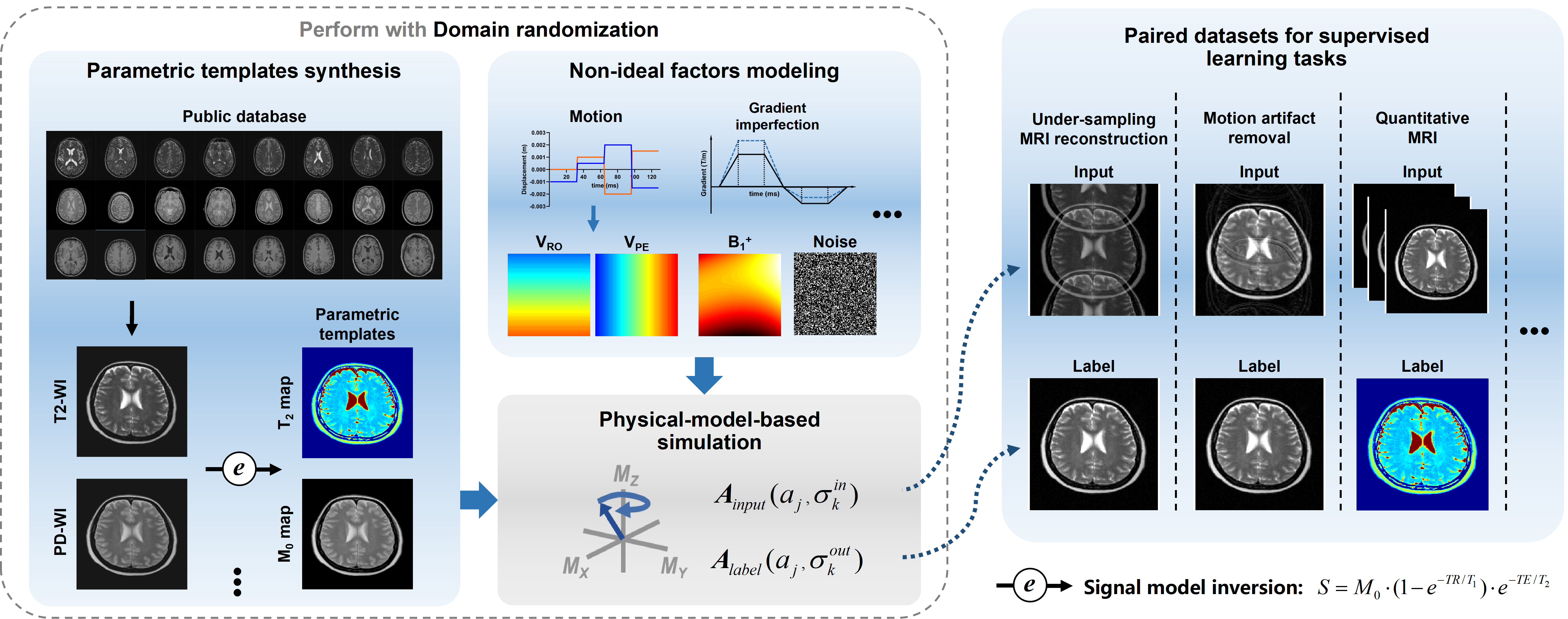
Use of synthetic data has provided a potential solution for addressing unavailable or insufficient training samples in deep learning-based magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). However, the challenge brought by domain gap between synthetic and real data is usually encountered, especially under complex experimental conditions. In this study, by combining Bloch simulation and general MRI models, we propose a framework for addressing the lack of training data in supervised learning scenarios, termed MOST-DL. A challenging application is demonstrated to verify the proposed framework and achieve motion-robust T2 mapping using single-shot overlapping-echo acquisition. We decompose the process into two main steps: (1) calibrationless parallel reconstruction for ultra-fast pulse sequence and (2) intra-shot motion correction for T2 mapping. To bridge the domain gap, realistic textures from a public database and various imperfection simulations were explored. The neural network was first trained with pure synthetic data and then evaluated with in vivo human brain. Both simulation and in vivo experiments show that the MOST-DL method significantly reduces ghosting and motion artifacts in T2 maps in the presence of unpredictable subject movement and has the potential to be applied to motion-prone patients in the clinic.
PDF Abstract