Multi-Task Learning with Multi-Query Transformer for Dense Prediction
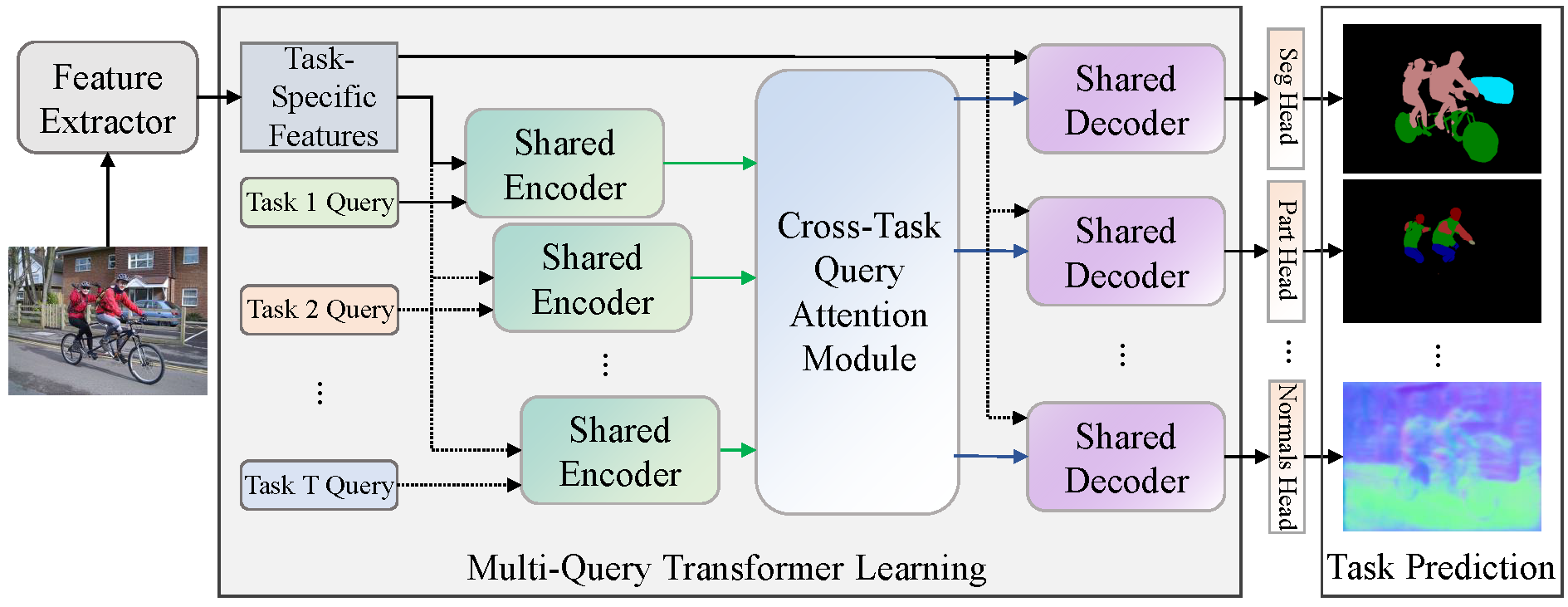
Previous multi-task dense prediction studies developed complex pipelines such as multi-modal distillations in multiple stages or searching for task relational contexts for each task. The core insight beyond these methods is to maximize the mutual effects of each task. Inspired by the recent query-based Transformers, we propose a simple pipeline named Multi-Query Transformer (MQTransformer) that is equipped with multiple queries from different tasks to facilitate the reasoning among multiple tasks and simplify the cross-task interaction pipeline. Instead of modeling the dense per-pixel context among different tasks, we seek a task-specific proxy to perform cross-task reasoning via multiple queries where each query encodes the task-related context. The MQTransformer is composed of three key components: shared encoder, cross-task query attention module and shared decoder. We first model each task with a task-relevant query. Then both the task-specific feature output by the feature extractor and the task-relevant query are fed into the shared encoder, thus encoding the task-relevant query from the task-specific feature. Secondly, we design a cross-task query attention module to reason the dependencies among multiple task-relevant queries; this enables the module to only focus on the query-level interaction. Finally, we use a shared decoder to gradually refine the image features with the reasoned query features from different tasks. Extensive experiment results on two dense prediction datasets (NYUD-v2 and PASCAL-Context) show that the proposed method is an effective approach and achieves state-of-the-art results. Code and models are available at https://github.com/yangyangxu0/MQTransformer.
PDF Abstract