Multi-Task Temporal Shift Attention Networks for On-Device Contactless Vitals Measurement
Telehealth and remote health monitoring have become increasingly important during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic and it is widely expected that this will have a lasting impact on healthcare practices. These tools can help reduce the risk of exposing patients and medical staff to infection, make healthcare services more accessible, and allow providers to see more patients. However, objective measurement of vital signs is challenging without direct contact with a patient. We present a video-based and on-device optical cardiopulmonary vital sign measurement approach. It leverages a novel multi-task temporal shift convolutional attention network (MTTS-CAN) and enables real-time cardiovascular and respiratory measurements on mobile platforms. We evaluate our system on an Advanced RISC Machine (ARM) CPU and achieve state-of-the-art accuracy while running at over 150 frames per second which enables real-time applications. Systematic experimentation on large benchmark datasets reveals that our approach leads to substantial (20%-50%) reductions in error and generalizes well across datasets.
PDF Abstract NeurIPS 2020 PDF NeurIPS 2020 Abstract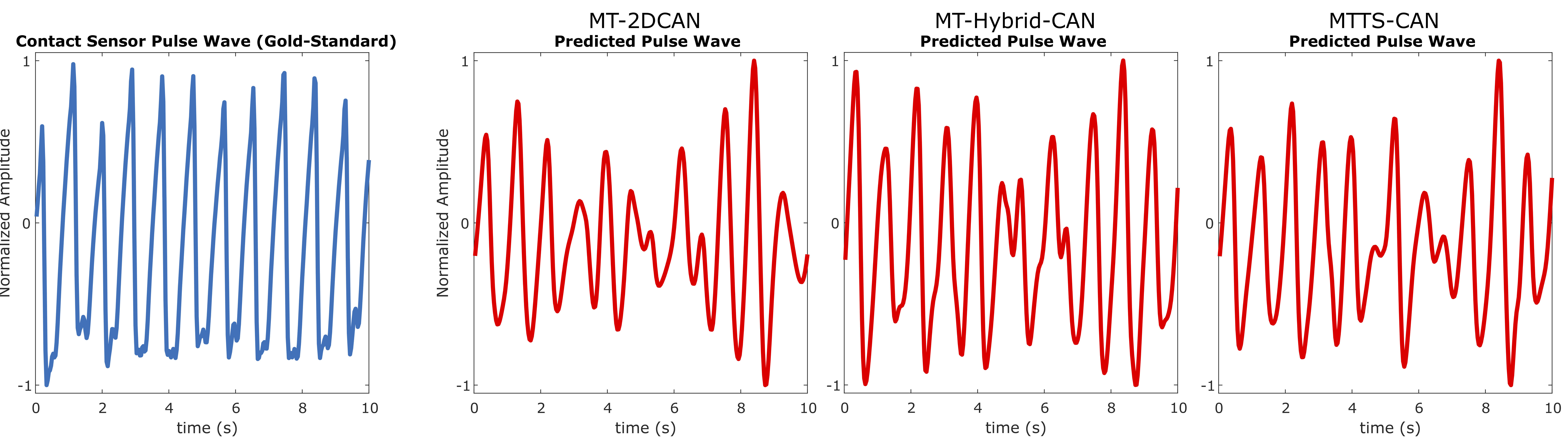



 UBFC-rPPG
UBFC-rPPG
 MMSE-HR
MMSE-HR
