On the Importance of Gradients for Detecting Distributional Shifts in the Wild
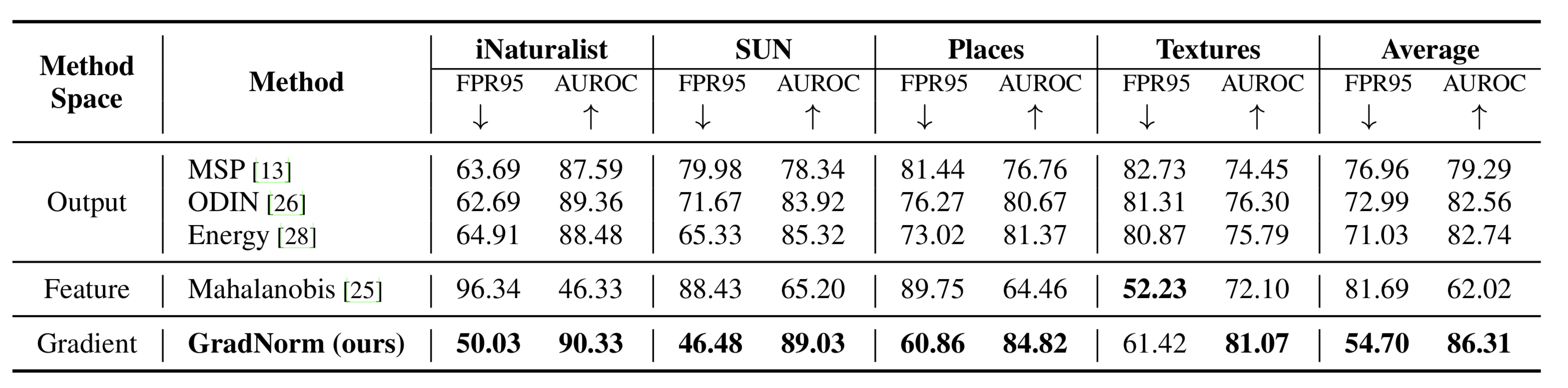
Detecting out-of-distribution (OOD) data has become a critical component in ensuring the safe deployment of machine learning models in the real world. Existing OOD detection approaches primarily rely on the output or feature space for deriving OOD scores, while largely overlooking information from the gradient space. In this paper, we present GradNorm, a simple and effective approach for detecting OOD inputs by utilizing information extracted from the gradient space. GradNorm directly employs the vector norm of gradients, backpropagated from the KL divergence between the softmax output and a uniform probability distribution. Our key idea is that the magnitude of gradients is higher for in-distribution (ID) data than that for OOD data, making it informative for OOD detection. GradNorm demonstrates superior performance, reducing the average FPR95 by up to 16.33% compared to the previous best method.
PDF Abstract NeurIPS 2021 PDF NeurIPS 2021 AbstractResults from the Paper
| Task | Dataset | Model | Metric Name | Metric Value | Global Rank | Benchmark |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Out-of-Distribution Detection | ImageNet-1k vs iNaturalist | GradNorm | FPR95 | 50.03 | # 19 | |
| Out-of-Distribution Detection | ImageNet-1k vs Places | GradNorm (ResNetv2-101) | FPR95 | 60.86 | # 17 | |
| Out-of-Distribution Detection | ImageNet-1k vs SUN | GradNorm (ResNetv2-101) | FPR95 | 46.48 | # 12 | |
| Out-of-Distribution Detection | ImageNet-1k vs Textures | GradNorm (ResNetv2-101) | FPR95 | 61.42 | # 25 |






 Places
Places
 iNaturalist
iNaturalist
 Places365
Places365
 Shifts
Shifts
 ImageNet-1k vs Textures
ImageNet-1k vs Textures
 ImageNet-1k vs iNaturalist
ImageNet-1k vs iNaturalist
 ImageNet-1k vs Places
ImageNet-1k vs Places
 ImageNet-1k vs SUN
ImageNet-1k vs SUN
