PAConv: Position Adaptive Convolution with Dynamic Kernel Assembling on Point Clouds
We introduce Position Adaptive Convolution (PAConv), a generic convolution operation for 3D point cloud processing. The key of PAConv is to construct the convolution kernel by dynamically assembling basic weight matrices stored in Weight Bank, where the coefficients of these weight matrices are self-adaptively learned from point positions through ScoreNet. In this way, the kernel is built in a data-driven manner, endowing PAConv with more flexibility than 2D convolutions to better handle the irregular and unordered point cloud data. Besides, the complexity of the learning process is reduced by combining weight matrices instead of brutally predicting kernels from point positions. Furthermore, different from the existing point convolution operators whose network architectures are often heavily engineered, we integrate our PAConv into classical MLP-based point cloud pipelines without changing network configurations. Even built on simple networks, our method still approaches or even surpasses the state-of-the-art models, and significantly improves baseline performance on both classification and segmentation tasks, yet with decent efficiency. Thorough ablation studies and visualizations are provided to understand PAConv. Code is released on https://github.com/CVMI-Lab/PAConv.
PDF Abstract CVPR 2021 PDF CVPR 2021 Abstract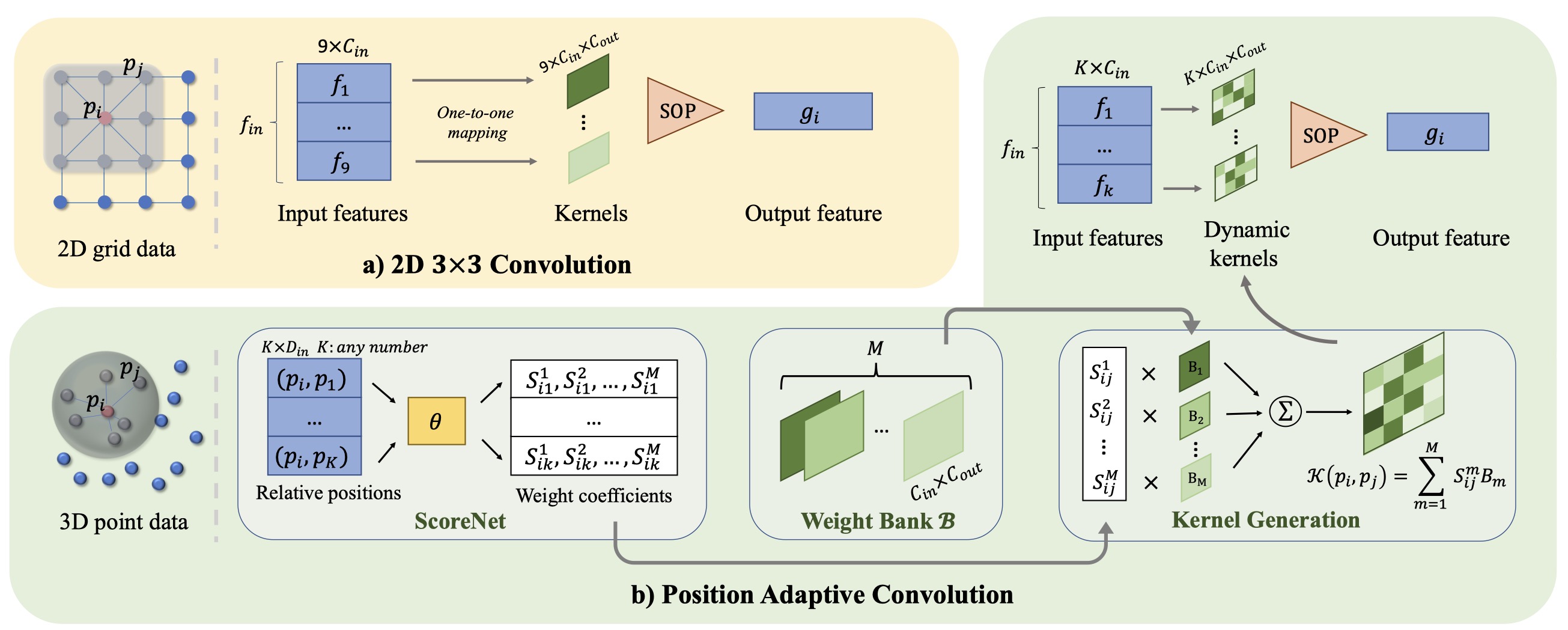








 ModelNet
ModelNet
 S3DIS
S3DIS
 IntrA
IntrA
 PointCloud-C
PointCloud-C
