Real-time Human-Centric Segmentation for Complex Video Scenes
Most existing video tasks related to "human" focus on the segmentation of salient humans, ignoring the unspecified others in the video. Few studies have focused on segmenting and tracking all humans in a complex video, including pedestrians and humans of other states (e.g., seated, riding, or occluded). In this paper, we propose a novel framework, abbreviated as HVISNet, that segments and tracks all presented people in given videos based on a one-stage detector. To better evaluate complex scenes, we offer a new benchmark called HVIS (Human Video Instance Segmentation), which comprises 1447 human instance masks in 805 high-resolution videos in diverse scenes. Extensive experiments show that our proposed HVISNet outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in terms of accuracy at a real-time inference speed (30 FPS), especially on complex video scenes. We also notice that using the center of the bounding box to distinguish different individuals severely deteriorates the segmentation accuracy, especially in heavily occluded conditions. This common phenomenon is referred to as the ambiguous positive samples problem. To alleviate this problem, we propose a mechanism named Inner Center Sampling to improve the accuracy of instance segmentation. Such a plug-and-play inner center sampling mechanism can be incorporated in any instance segmentation models based on a one-stage detector to improve the performance. In particular, it gains 4.1 mAP improvement on the state-of-the-art method in the case of occluded humans. Code and data are available at https://github.com/IIGROUP/HVISNet.
PDF Abstract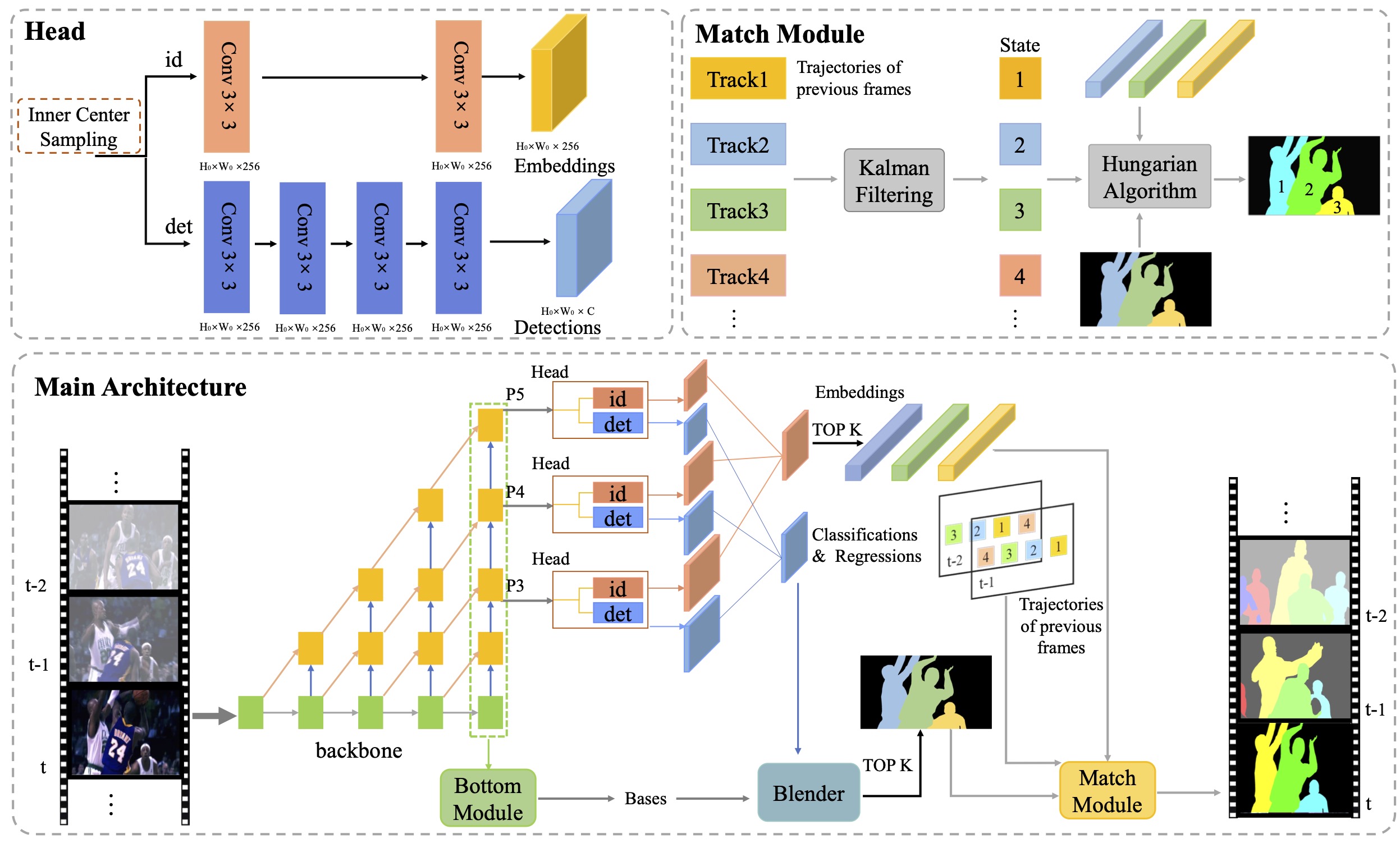





 MS COCO
MS COCO
 DAVIS
DAVIS
 YouTube-VIS 2019
YouTube-VIS 2019
 OCHuman
OCHuman