Reinforcement Learning-powered Semantic Communication via Semantic Similarity
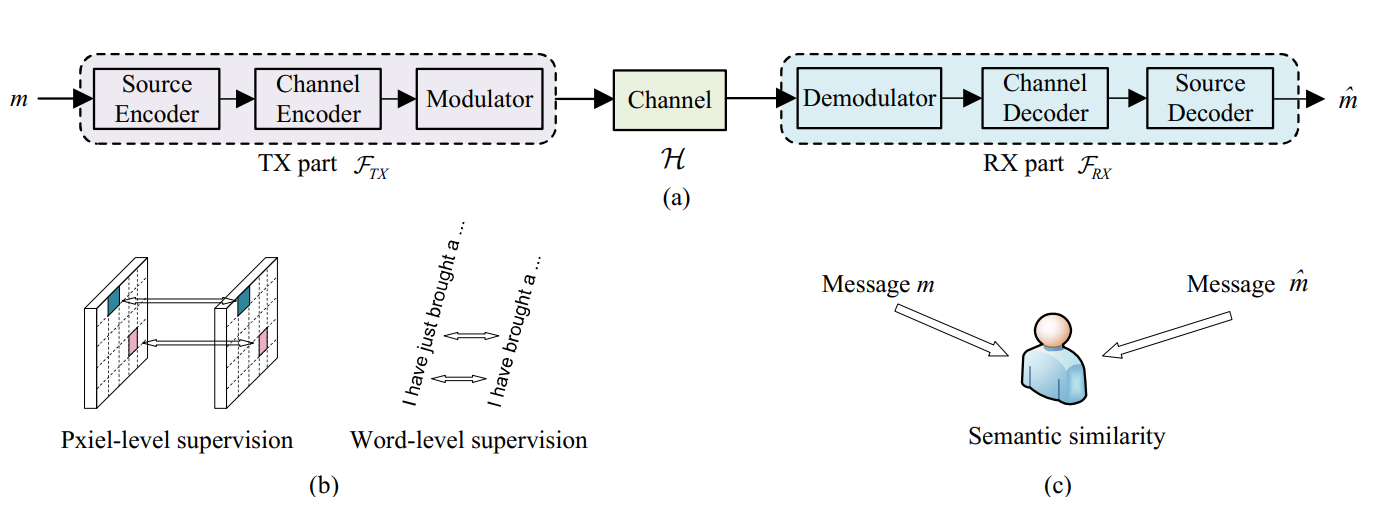
We introduce a new semantic communication mechanism - SemanticRL, whose key idea is to preserve the semantic information instead of strictly securing the bit-level precision. Unlike previous methods that mainly concentrate on the network or structure design, we revisit the learning process and point out the semantic blindness of commonly used objective functions. To address this semantic gap, we introduce a schematic shift that learns from semantic similarity, instead of relying on conventional paired bit-level supervisions like cross entropy and bit error rate. However, developing such a semantic communication system is indeed a nontrivial task considering the non-differentiability of most semantic metrics as well as the instability from noisy channels. To further resolve these issues, we put forward a self-critic reinforcement learning (RL) solution which allows an efficient and stable learning on any user-defined semantic measurement, and take a step further to simultaneously tackle the non-differentiable semantic channel optimization problem via self-critic stochastic iterative updating (SCSIU) training on the decoupled semantic transceiver. We have firstly tested the proposed method in the challenging European-parliament dataset, which confirms the superiority of our method in revealing the semantic meanings, and better handling the semantic noise. Apart from the experimental results, we further provide an in-depth look at how the semantic model behaves, along with its superb generalization ability in real-life examples. An RL-based image transmission extension is also exemplified, so as to prove the generalization ability and motivate future discussion.
PDF Abstract