Reliable Label Correction is a Good Booster When Learning with Extremely Noisy Labels
Learning with noisy labels has aroused much research interest since data annotations, especially for large-scale datasets, may be inevitably imperfect. Recent approaches resort to a semi-supervised learning problem by dividing training samples into clean and noisy sets. This paradigm, however, is prone to significant degeneration under heavy label noise, as the number of clean samples is too small for conventional methods to behave well. In this paper, we introduce a novel framework, termed as LC-Booster, to explicitly tackle learning under extreme noise. The core idea of LC-Booster is to incorporate label correction into the sample selection, so that more purified samples, through the reliable label correction, can be utilized for training, thereby alleviating the confirmation bias. Experiments show that LC-Booster advances state-of-the-art results on several noisy-label benchmarks, including CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100, Clothing1M and WebVision. Remarkably, under the extreme 90\% noise ratio, LC-Booster achieves 92.9\% and 48.4\% accuracy on CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100, surpassing state-of-the-art methods by a large margin.
PDF Abstract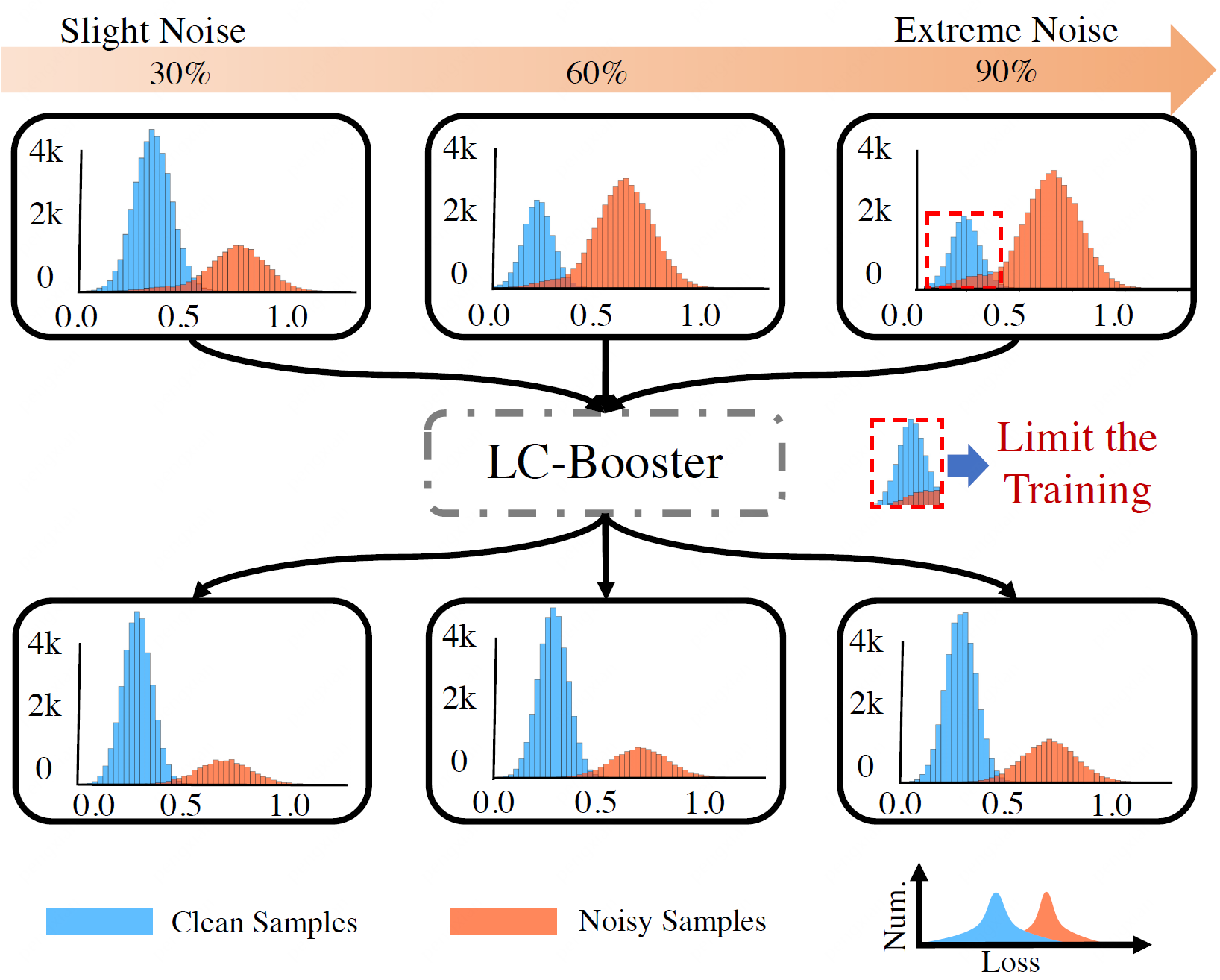


 CIFAR-10
CIFAR-10
 CIFAR-100
CIFAR-100
 Clothing1M
Clothing1M
 WebVision
WebVision