Rethinking Bias-Variance Trade-off for Generalization of Neural Networks
The classical bias-variance trade-off predicts that bias decreases and variance increase with model complexity, leading to a U-shaped risk curve. Recent work calls this into question for neural networks and other over-parameterized models, for which it is often observed that larger models generalize better. We provide a simple explanation for this by measuring the bias and variance of neural networks: while the bias is monotonically decreasing as in the classical theory, the variance is unimodal or bell-shaped: it increases then decreases with the width of the network. We vary the network architecture, loss function, and choice of dataset and confirm that variance unimodality occurs robustly for all models we considered. The risk curve is the sum of the bias and variance curves and displays different qualitative shapes depending on the relative scale of bias and variance, with the double descent curve observed in recent literature as a special case. We corroborate these empirical results with a theoretical analysis of two-layer linear networks with random first layer. Finally, evaluation on out-of-distribution data shows that most of the drop in accuracy comes from increased bias while variance increases by a relatively small amount. Moreover, we find that deeper models decrease bias and increase variance for both in-distribution and out-of-distribution data.
PDF Abstract ICML 2020 PDF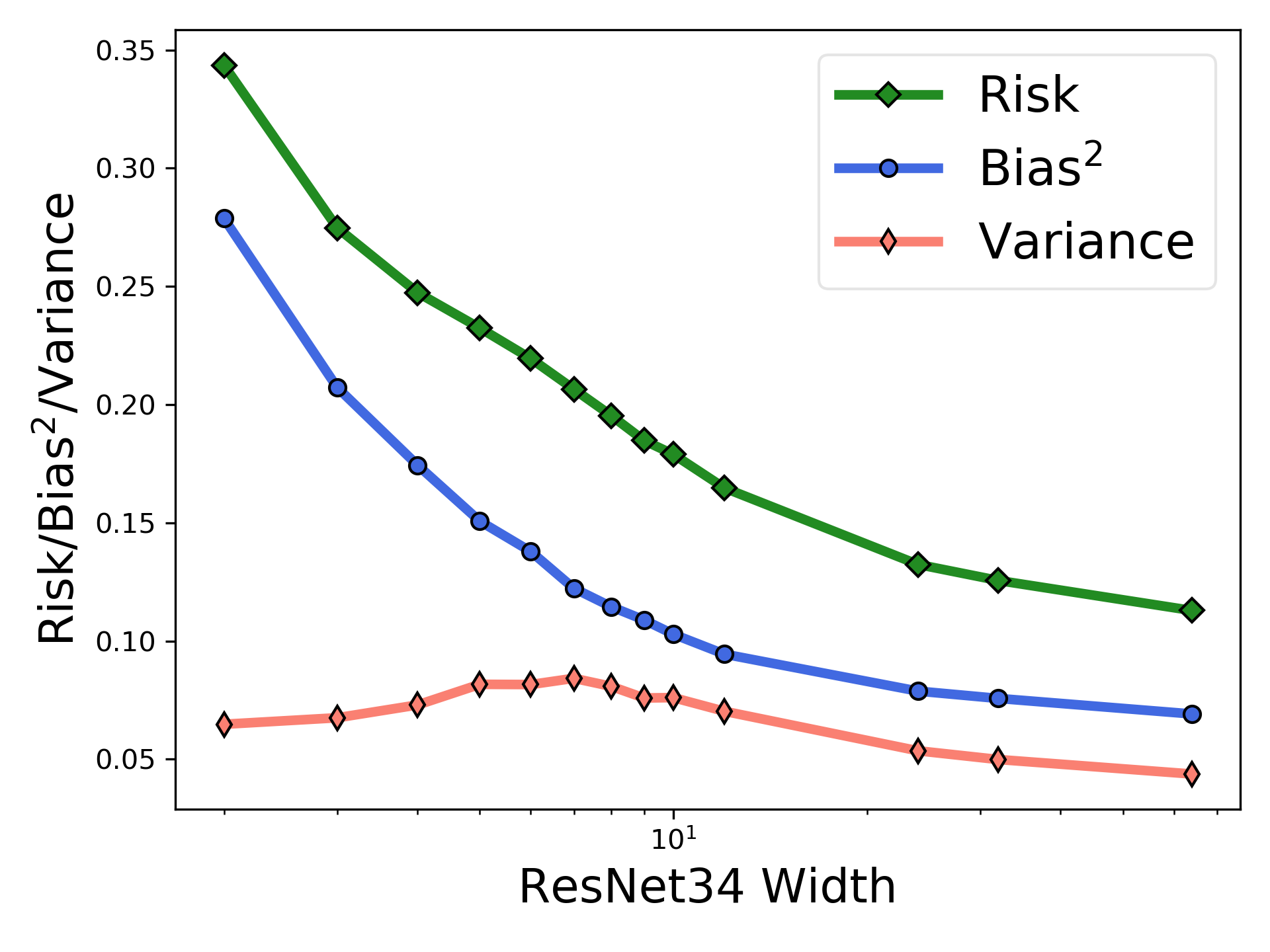

 CIFAR-10
CIFAR-10
 Fashion-MNIST
Fashion-MNIST