Robust universal neural vocoding
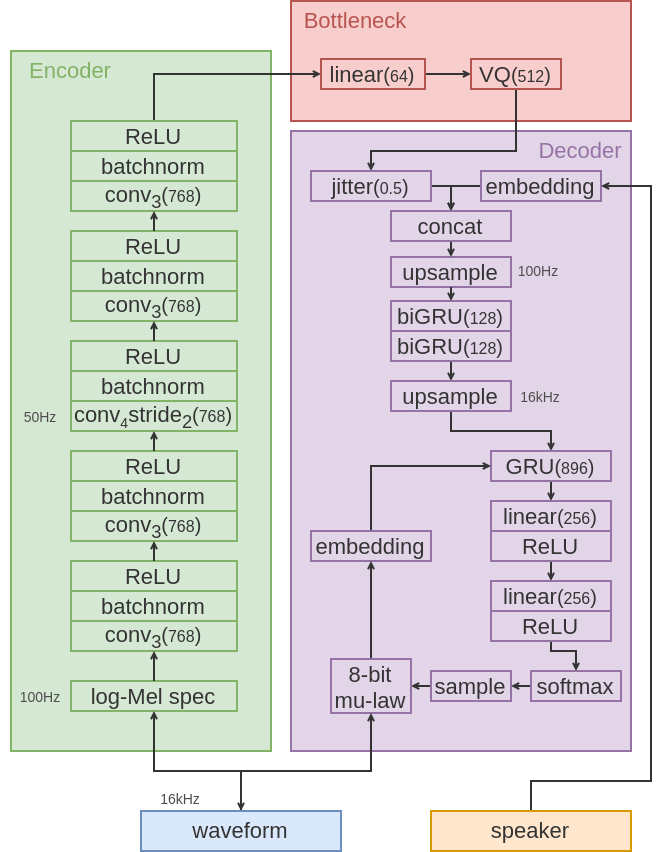
This paper introduces a robust universal neural vocoder trained with 74 speakers (comprised of both genders) coming from 17 languages. This vocoder is shown to be capable of generating speech of consistently good quality (98% relative mean MUSHRA when compared to natural speech) regardless of whether the input spectrogram comes from a speaker, style or recording condition seen during training or from an out-of-domain scenario. Together with the system, we present a full text-to-speech analysis of robustness of a number of implemented systems. The complexity of systems tested range from a convolutional neural networks-based system conditioned on linguistics to a recurrent neural networks-based system conditioned on mel-spectrograms. The analysis shows that convolutional neural networks-based systems are prone to occasional instabilities, while the recurrent approaches are significantly more stable and capable of providing universalizing robustness.
PDF Abstract