Roto-Translation Covariant Convolutional Networks for Medical Image Analysis
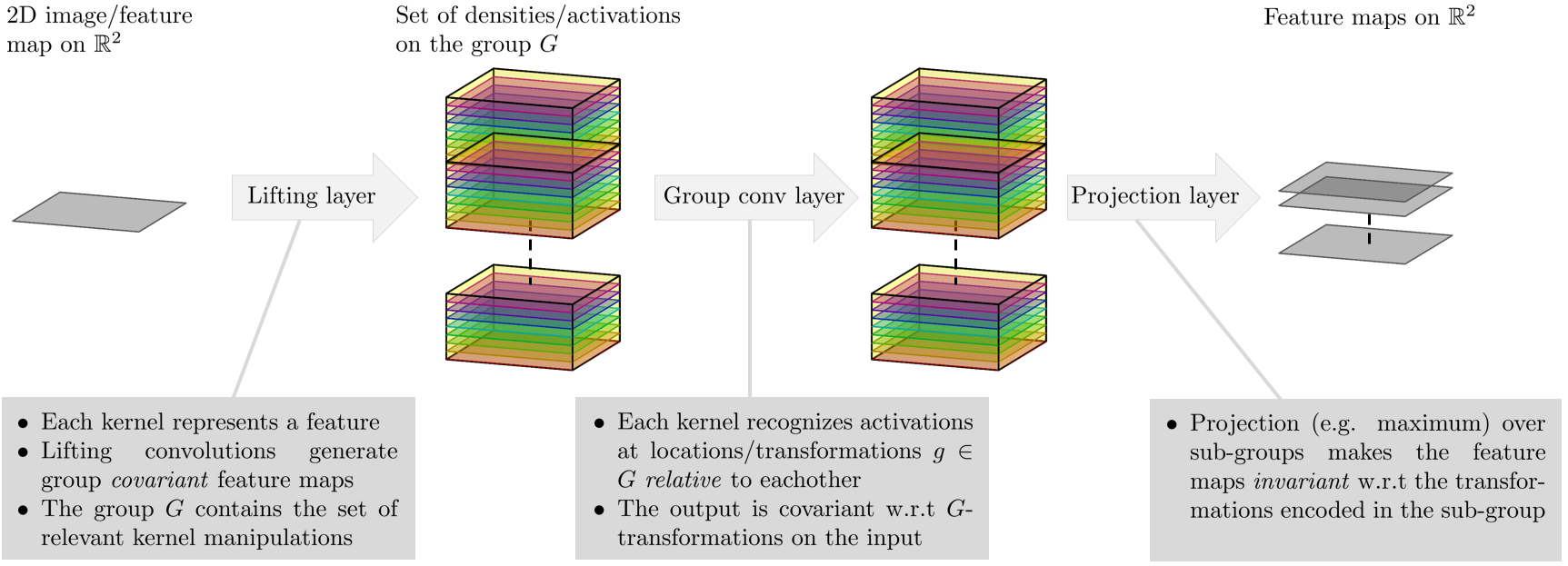
We propose a framework for rotation and translation covariant deep learning using $SE(2)$ group convolutions. The group product of the special Euclidean motion group $SE(2)$ describes how a concatenation of two roto-translations results in a net roto-translation. We encode this geometric structure into convolutional neural networks (CNNs) via $SE(2)$ group convolutional layers, which fit into the standard 2D CNN framework, and which allow to generically deal with rotated input samples without the need for data augmentation. We introduce three layers: a lifting layer which lifts a 2D (vector valued) image to an $SE(2)$-image, i.e., 3D (vector valued) data whose domain is $SE(2)$; a group convolution layer from and to an $SE(2)$-image; and a projection layer from an $SE(2)$-image to a 2D image. The lifting and group convolution layers are $SE(2)$ covariant (the output roto-translates with the input). The final projection layer, a maximum intensity projection over rotations, makes the full CNN rotation invariant. We show with three different problems in histopathology, retinal imaging, and electron microscopy that with the proposed group CNNs, state-of-the-art performance can be achieved, without the need for data augmentation by rotation and with increased performance compared to standard CNNs that do rely on augmentation.
PDF Abstract