Self-supervised Auxiliary Learning with Meta-paths for Heterogeneous Graphs
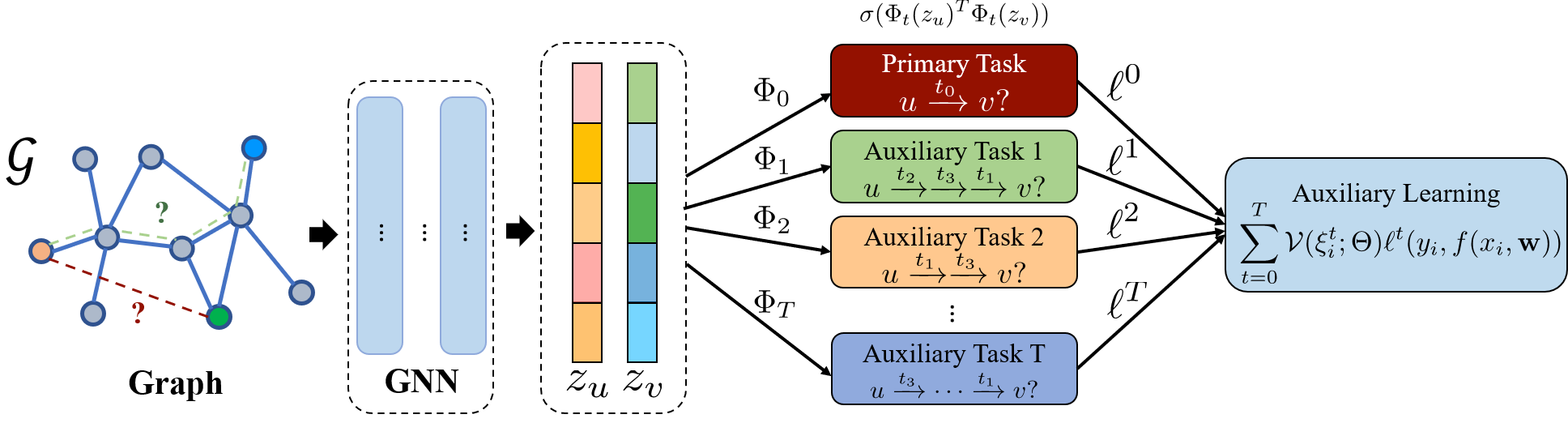
Graph neural networks have shown superior performance in a wide range of applications providing a powerful representation of graph-structured data. Recent works show that the representation can be further improved by auxiliary tasks. However, the auxiliary tasks for heterogeneous graphs, which contain rich semantic information with various types of nodes and edges, have less explored in the literature. In this paper, to learn graph neural networks on heterogeneous graphs we propose a novel self-supervised auxiliary learning method using meta-paths, which are composite relations of multiple edge types. Our proposed method is learning to learn a primary task by predicting meta-paths as auxiliary tasks. This can be viewed as a type of meta-learning. The proposed method can identify an effective combination of auxiliary tasks and automatically balance them to improve the primary task. Our methods can be applied to any graph neural networks in a plug-in manner without manual labeling or additional data. The experiments demonstrate that the proposed method consistently improves the performance of link prediction and node classification on heterogeneous graphs.
PDF Abstract NeurIPS 2020 PDF NeurIPS 2020 Abstract