Self-Supervised Learning Disentangled Group Representation as Feature
A good visual representation is an inference map from observations (images) to features (vectors) that faithfully reflects the hidden modularized generative factors (semantics). In this paper, we formulate the notion of "good" representation from a group-theoretic view using Higgins' definition of disentangled representation, and show that existing Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) only disentangles simple augmentation features such as rotation and colorization, thus unable to modularize the remaining semantics. To break the limitation, we propose an iterative SSL algorithm: Iterative Partition-based Invariant Risk Minimization (IP-IRM), which successfully grounds the abstract semantics and the group acting on them into concrete contrastive learning. At each iteration, IP-IRM first partitions the training samples into two subsets that correspond to an entangled group element. Then, it minimizes a subset-invariant contrastive loss, where the invariance guarantees to disentangle the group element. We prove that IP-IRM converges to a fully disentangled representation and show its effectiveness on various benchmarks. Codes are available at https://github.com/Wangt-CN/IP-IRM.
PDF Abstract NeurIPS 2021 PDF NeurIPS 2021 Abstract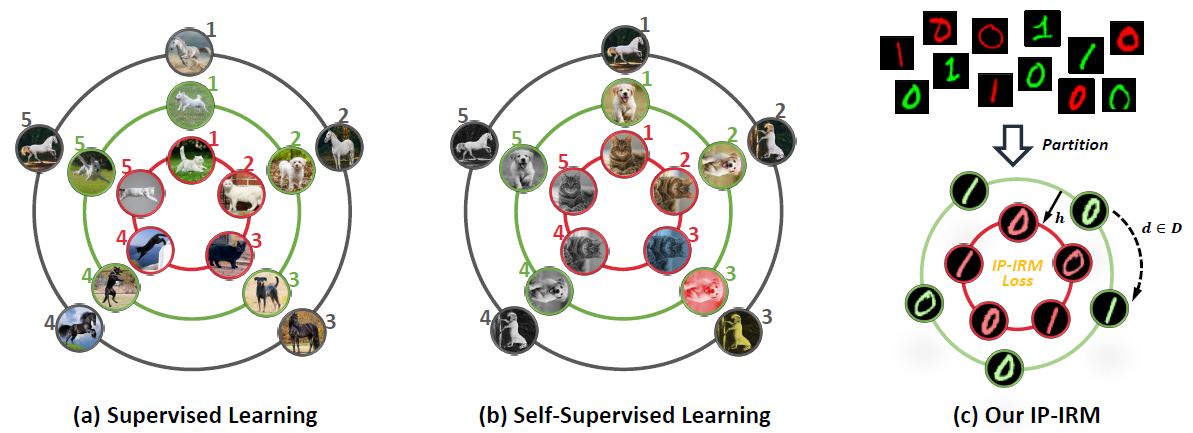




 CIFAR-10
CIFAR-10
 CIFAR-100
CIFAR-100
 Oxford 102 Flower
Oxford 102 Flower
 STL-10
STL-10
 DTD
DTD