Shortest Paths in Graphs with Matrix-Valued Edges: Concepts, Algorithm and Application to 3D Multi-Shape Analysis
Finding shortest paths in a graph is relevant for numerous problems in computer vision and graphics, including image segmentation, shape matching, or the computation of geodesic distances on discrete surfaces. Traditionally, the concept of a shortest path is considered for graphs with scalar edge weights, which makes it possible to compute the length of a path by adding up the individual edge weights. Yet, graphs with scalar edge weights are severely limited in their expressivity, since oftentimes edges are used to encode significantly more complex interrelations. In this work we compensate for this modelling limitation and introduce the novel graph-theoretic concept of a shortest path in a graph with matrix-valued edges. To this end, we define a meaningful way for quantifying the path length for matrix-valued edges, and we propose a simple yet effective algorithm to compute the respective shortest path. While our formalism is universal and thus applicable to a wide range of settings in vision, graphics and beyond, we focus on demonstrating its merits in the context of 3D multi-shape analysis.
PDF Abstract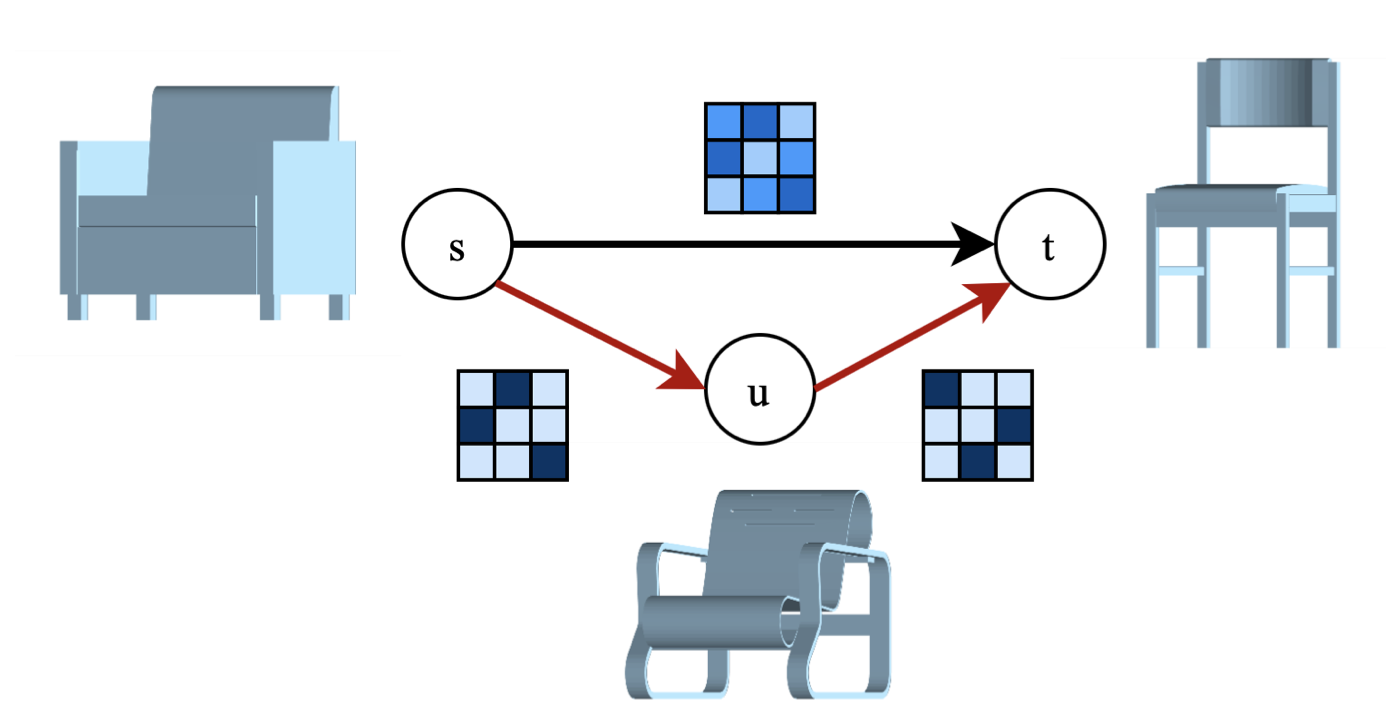


 ShapeNet
ShapeNet