Sparse Bounded Degree Sum of Squares Optimization for Certifiably Globally Optimal Rotation Averaging
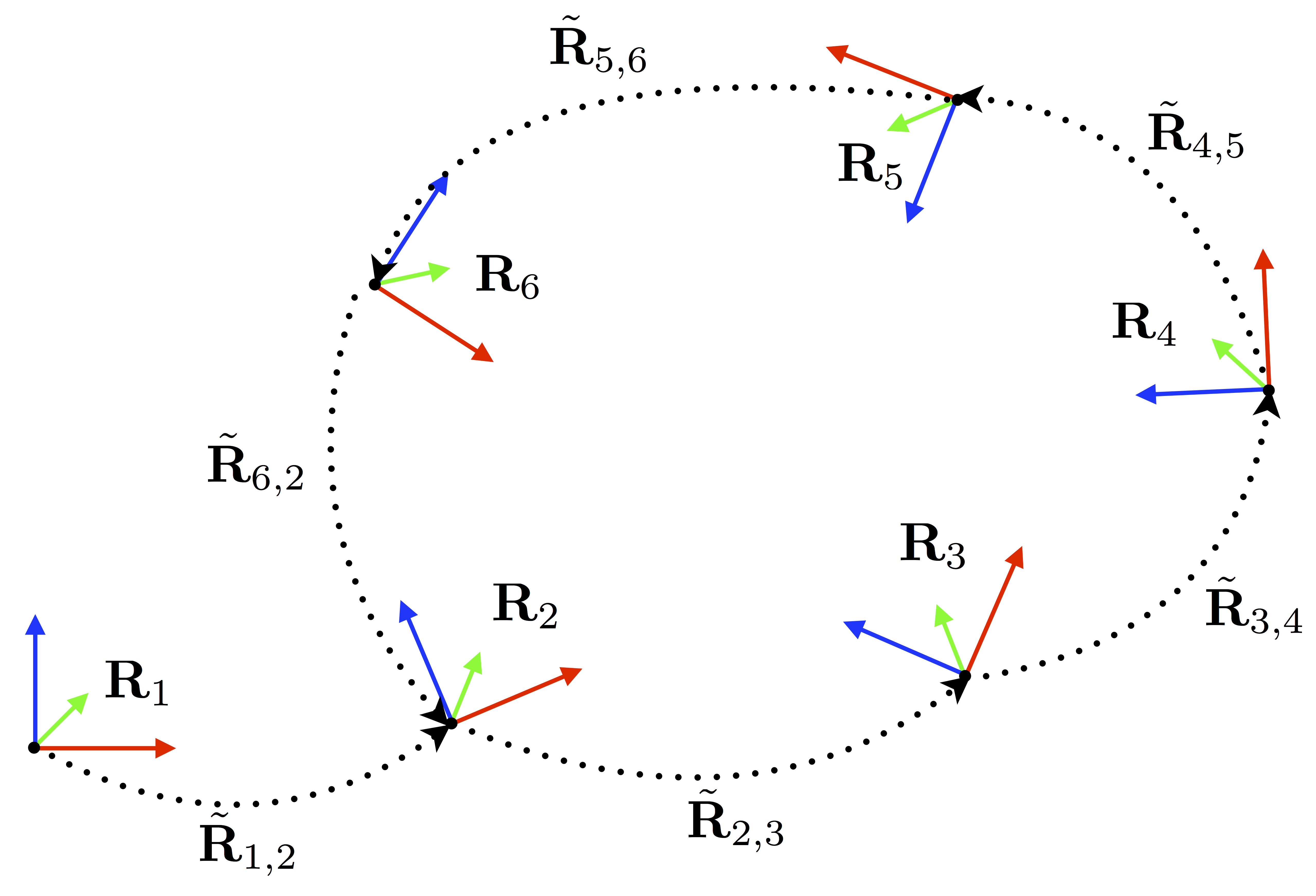
Estimating unknown rotations from noisy measurements is an important step in SfM and other 3D vision tasks. Typically, local optimization methods susceptible to returning suboptimal local minima are used to solve the rotation averaging problem. A new wave of approaches that leverage convex relaxations have provided the first formal guarantees of global optimality for state estimation techniques involving SO(3). However, most of these guarantees are only applicable when the measurement error introduced by noise is within a certain bound that depends on the problem instance's structure. In this paper, we cast rotation averaging as a polynomial optimization problem over unit quaternions to produce the first rotation averaging method that is formally guaranteed to provide a certifiably globally optimal solution for \textit{any} problem instance. This is achieved by formulating and solving a sparse convex sum of squares (SOS) relaxation of the problem. We provide an open source implementation of our algorithm and experiments, demonstrating the benefits of our globally optimal approach.
PDF Abstract