Speech Gesture Generation from the Trimodal Context of Text, Audio, and Speaker Identity
For human-like agents, including virtual avatars and social robots, making proper gestures while speaking is crucial in human--agent interaction. Co-speech gestures enhance interaction experiences and make the agents look alive. However, it is difficult to generate human-like gestures due to the lack of understanding of how people gesture. Data-driven approaches attempt to learn gesticulation skills from human demonstrations, but the ambiguous and individual nature of gestures hinders learning. In this paper, we present an automatic gesture generation model that uses the multimodal context of speech text, audio, and speaker identity to reliably generate gestures. By incorporating a multimodal context and an adversarial training scheme, the proposed model outputs gestures that are human-like and that match with speech content and rhythm. We also introduce a new quantitative evaluation metric for gesture generation models. Experiments with the introduced metric and subjective human evaluation showed that the proposed gesture generation model is better than existing end-to-end generation models. We further confirm that our model is able to work with synthesized audio in a scenario where contexts are constrained, and show that different gesture styles can be generated for the same speech by specifying different speaker identities in the style embedding space that is learned from videos of various speakers. All the code and data is available at https://github.com/ai4r/Gesture-Generation-from-Trimodal-Context.
PDF Abstract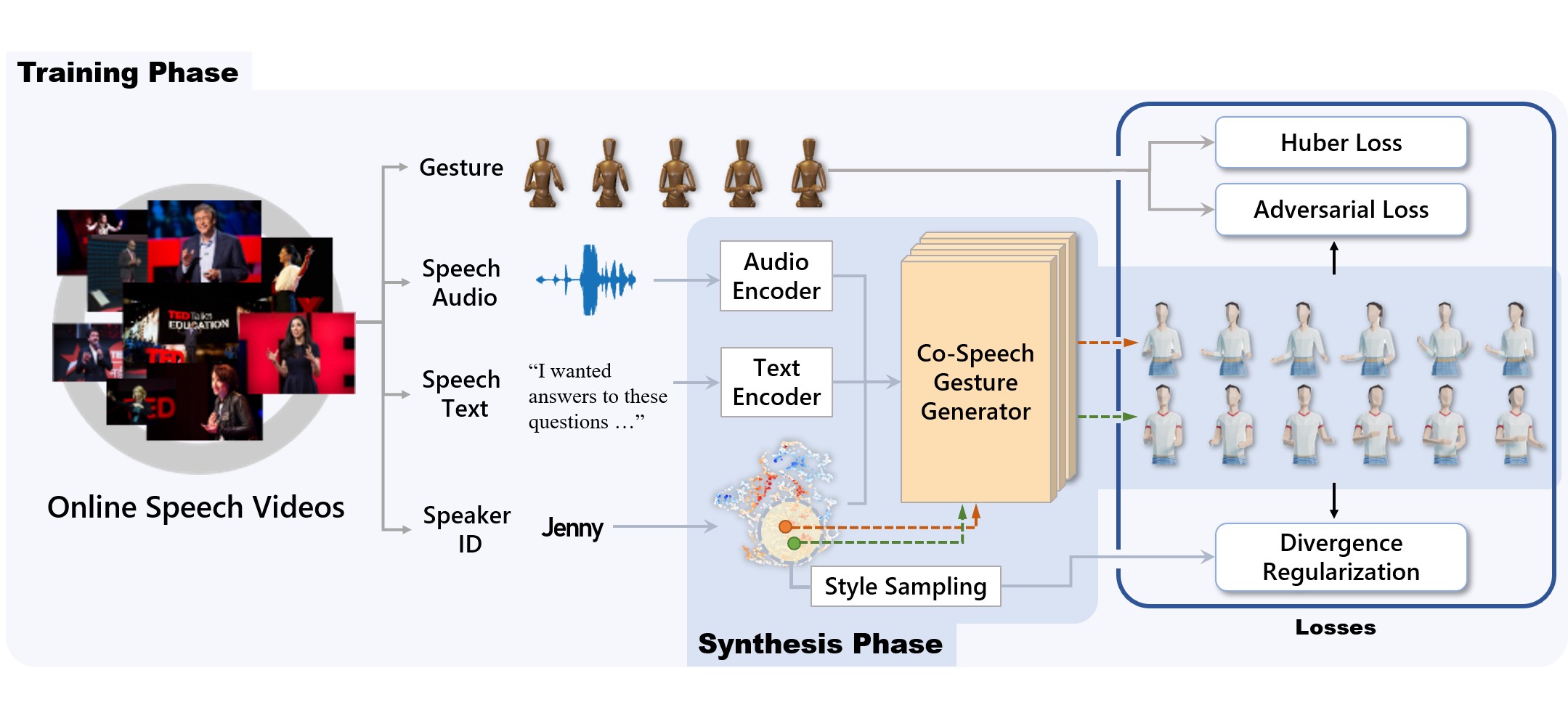





 BEAT
BEAT
 BEAT2
BEAT2
