The Devil is in the Details: Delving into Unbiased Data Processing for Human Pose Estimation
Being a fundamental component in training and inference, data processing has not been systematically considered in human pose estimation community, to the best of our knowledge. In this paper, we focus on this problem and find that the devil of human pose estimation evolution is in the biased data processing. Specifically, by investigating the standard data processing in state-of-the-art approaches mainly including coordinate system transformation and keypoint format transformation (i.e., encoding and decoding), we find that the results obtained by common flipping strategy are unaligned with the original ones in inference. Moreover, there is a statistical error in some keypoint format transformation methods. Two problems couple together, significantly degrade the pose estimation performance and thus lay a trap for the research community. This trap has given bone to many suboptimal remedies, which are always unreported, confusing but influential. By causing failure in reproduction and unfair in comparison, the unreported remedies seriously impedes the technological development. To tackle this dilemma from the source, we propose Unbiased Data Processing (UDP) consist of two technique aspect for the two aforementioned problems respectively (i.e., unbiased coordinate system transformation and unbiased keypoint format transformation). As a model-agnostic approach and a superior solution, UDP successfully pushes the performance boundary of human pose estimation and offers a higher and more reliable baseline for research community. Code is public available in https://github.com/HuangJunJie2017/UDP-Pose
PDF Abstract CVPR 2020 PDF CVPR 2020 Abstract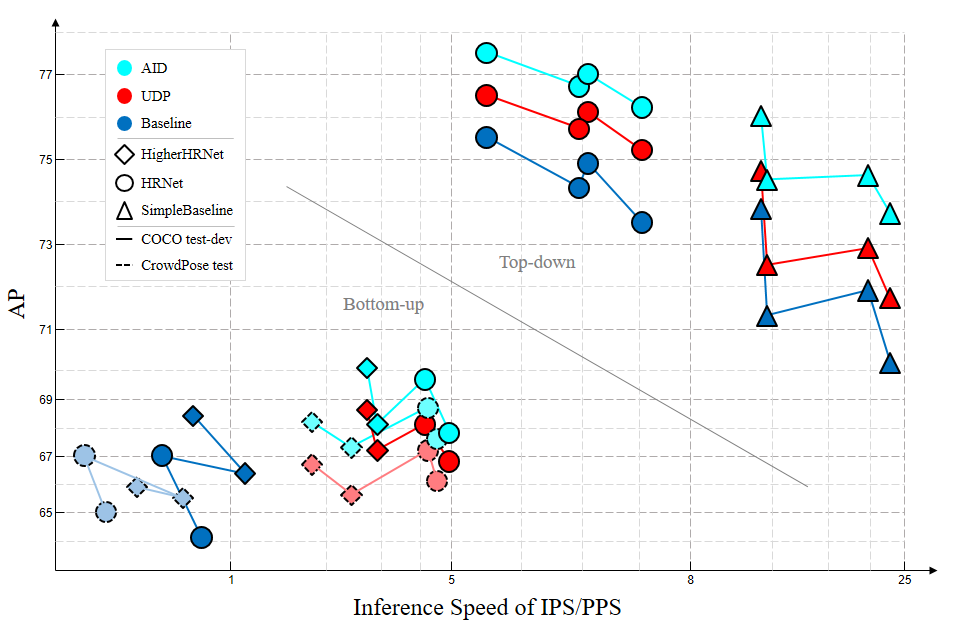





 MS COCO
MS COCO
