Towards Verifying the Geometric Robustness of Large-scale Neural Networks
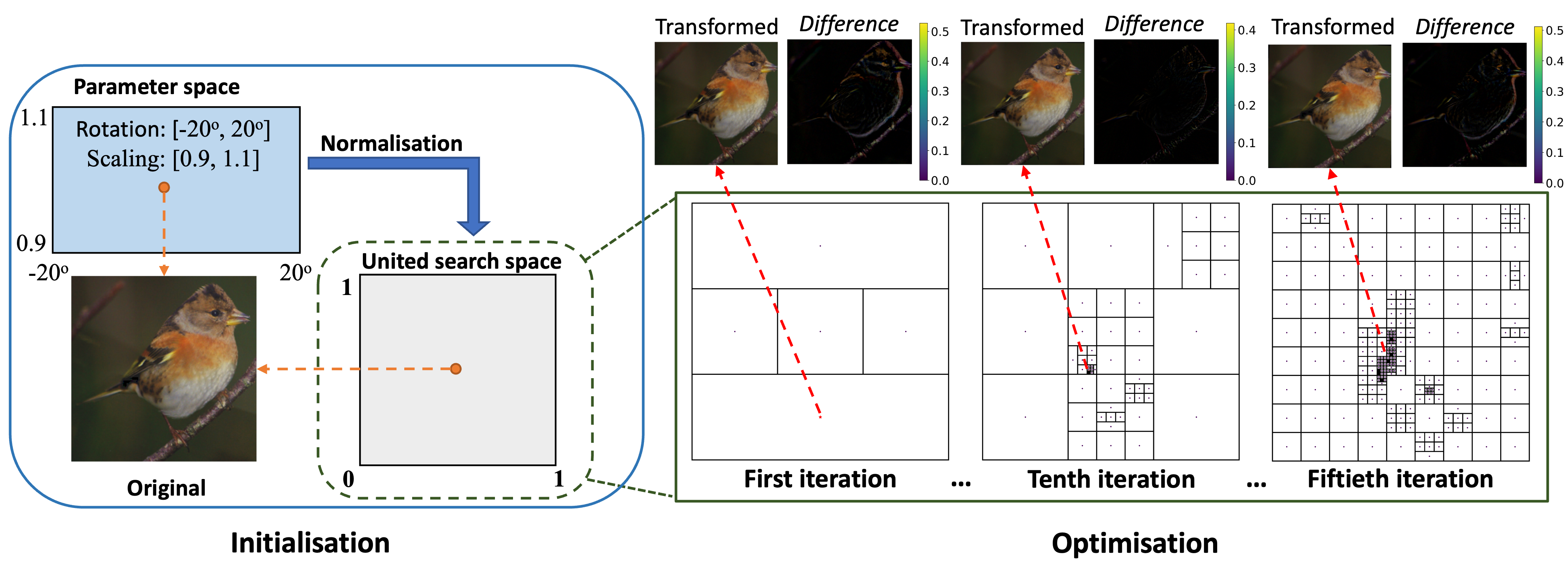
Deep neural networks (DNNs) are known to be vulnerable to adversarial geometric transformation. This paper aims to verify the robustness of large-scale DNNs against the combination of multiple geometric transformations with a provable guarantee. Given a set of transformations (e.g., rotation, scaling, etc.), we develop GeoRobust, a black-box robustness analyser built upon a novel global optimisation strategy, for locating the worst-case combination of transformations that affect and even alter a network's output. GeoRobust can provide provable guarantees on finding the worst-case combination based on recent advances in Lipschitzian theory. Due to its black-box nature, GeoRobust can be deployed on large-scale DNNs regardless of their architectures, activation functions, and the number of neurons. In practice, GeoRobust can locate the worst-case geometric transformation with high precision for the ResNet50 model on ImageNet in a few seconds on average. We examined 18 ImageNet classifiers, including the ResNet family and vision transformers, and found a positive correlation between the geometric robustness of the networks and the parameter numbers. We also observe that increasing the depth of DNN is more beneficial than increasing its width in terms of improving its geometric robustness. Our tool GeoRobust is available at https://github.com/TrustAI/GeoRobust.
PDF Abstract