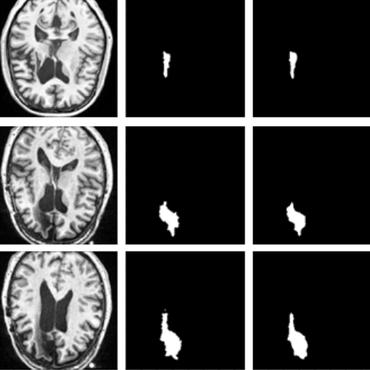
X-Net: Brain Stroke Lesion Segmentation Based on Depthwise Separable Convolution and Long-range Dependencies
The morbidity of brain stroke increased rapidly in the past few years. To help specialists in lesion measurements and treatment planning, automatic segmentation methods are critically required for clinical practices. Recently, approaches based on deep learning and methods for contextual information extraction have served in many image segmentation tasks. However, their performances are limited due to the insufficient training of a large number of parameters, which sometimes fail in capturing long-range dependencies. To address these issues, we propose a depthwise separable convolution based X-Net that designs a nonlocal operation namely Feature Similarity Module (FSM) to capture long-range dependencies. The adopted depthwise convolution allows to reduce the network size, while the developed FSM provides a more effective, dense contextual information extraction and thus facilitates better segmentation. The effectiveness of X-Net was evaluated on an open dataset Anatomical Tracings of Lesions After Stroke (ATLAS) with superior performance achieved compared to other six state-of-the-art approaches. We make our code and models available at https://github.com/Andrewsher/X-Net.
PDF Abstract