Search Results for author: Julian Straub
Found 22 papers, 6 papers with code
A Mixture of Manhattan Frames: Beyond the Manhattan World
no code implementations • CVPR 2014 • Julian Straub, Guy Rosman, Oren Freifeld, John J. Leonard, John W. Fisher III
Traditional approaches to scene representation exploit this phenomenon via the somewhat restrictive assumption that every plane is perpendicular to one of the axes of a single coordinate system.
Streaming, Distributed Variational Inference for Bayesian Nonparametrics
no code implementations • NeurIPS 2015 • Trevor Campbell, Julian Straub, John W. Fisher III, Jonathan P. How
This paper presents a methodology for creating streaming, distributed inference algorithms for Bayesian nonparametric (BNP) models.
Semantically-Aware Aerial Reconstruction From Multi-Modal Data
no code implementations • ICCV 2015 • Randi Cabezas, Julian Straub, John W. Fisher III
We consider a methodology for integrating multiple sensors along with semantic information to enhance scene representations.
Efficient Global Point Cloud Alignment using Bayesian Nonparametric Mixtures
no code implementations • CVPR 2017 • Julian Straub, Trevor Campbell, Jonathan P. How, John W. Fisher III
Point cloud alignment is a common problem in computer vision and robotics, with applications ranging from 3D object recognition to reconstruction.
Small-Variance Nonparametric Clustering on the Hypersphere
no code implementations • CVPR 2015 • Julian Straub, Trevor Campbell, Jonathan P. How, John W. Fisher III
Based on the small-variance limit of Bayesian nonparametric von-Mises-Fisher (vMF) mixture distributions, we propose two new flexible and efficient k-means-like clustering algorithms for directional data such as surface normals.
Direction-Aware Semi-Dense SLAM
no code implementations • 18 Sep 2017 • Julian Straub, Randi Cabezas, John Leonard, John W. Fisher III
To aide simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM), future perception systems will incorporate forms of scene understanding.
Bayesian Nonparametric Modeling of Driver Behavior using HDP Split-Merge Sampling Algorithm
no code implementations • 27 Jan 2018 • Vadim Smolyakov, Julian Straub, Sue Zheng, John W. Fisher III
In a novel manner, we demonstrate how the sparsity of the personal road network of a driver in conjunction with a hierarchical topic model allows data driven predictions about destinations as well as likely road conditions.
DeepSDF: Learning Continuous Signed Distance Functions for Shape Representation
4 code implementations • CVPR 2019 • Jeong Joon Park, Peter Florence, Julian Straub, Richard Newcombe, Steven Lovegrove
In this work, we introduce DeepSDF, a learned continuous Signed Distance Function (SDF) representation of a class of shapes that enables high quality shape representation, interpolation and completion from partial and noisy 3D input data.
Habitat: A Platform for Embodied AI Research
13 code implementations • ICCV 2019 • Manolis Savva, Abhishek Kadian, Oleksandr Maksymets, Yili Zhao, Erik Wijmans, Bhavana Jain, Julian Straub, Jia Liu, Vladlen Koltun, Jitendra Malik, Devi Parikh, Dhruv Batra
We present Habitat, a platform for research in embodied artificial intelligence (AI).
 Ranked #2 on
PointGoal Navigation
on Gibson PointGoal Navigation
Ranked #2 on
PointGoal Navigation
on Gibson PointGoal Navigation
StereoDRNet: Dilated Residual Stereo Net
no code implementations • 3 Apr 2019 • Rohan Chabra, Julian Straub, Chris Sweeney, Richard Newcombe, Henry Fuchs
We propose a system that uses a convolution neural network (CNN) to estimate depth from a stereo pair followed by volumetric fusion of the predicted depth maps to produce a 3D reconstruction of a scene.
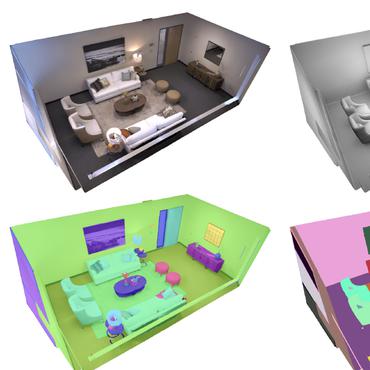
The Replica Dataset: A Digital Replica of Indoor Spaces
2 code implementations • 13 Jun 2019 • Julian Straub, Thomas Whelan, Lingni Ma, Yufan Chen, Erik Wijmans, Simon Green, Jakob J. Engel, Raul Mur-Artal, Carl Ren, Shobhit Verma, Anton Clarkson, Mingfei Yan, Brian Budge, Yajie Yan, Xiaqing Pan, June Yon, Yuyang Zou, Kimberly Leon, Nigel Carter, Jesus Briales, Tyler Gillingham, Elias Mueggler, Luis Pesqueira, Manolis Savva, Dhruv Batra, Hauke M. Strasdat, Renzo De Nardi, Michael Goesele, Steven Lovegrove, Richard Newcombe
We introduce Replica, a dataset of 18 highly photo-realistic 3D indoor scene reconstructions at room and building scale.
Insights on Visual Representations for Embodied Navigation Tasks
no code implementations • ICLR 2020 • Erik Wijmans, Julian Straub, Irfan Essa, Dhruv Batra, Judy Hoffman, Ari Morcos
Surprisingly, we find that slight differences in task have no measurable effect on the visual representation for both SqueezeNet and ResNet architectures.
Analyzing Visual Representations in Embodied Navigation Tasks
no code implementations • 12 Mar 2020 • Erik Wijmans, Julian Straub, Dhruv Batra, Irfan Essa, Judy Hoffman, Ari Morcos
Recent advances in deep reinforcement learning require a large amount of training data and generally result in representations that are often over specialized to the target task.
Deep Local Shapes: Learning Local SDF Priors for Detailed 3D Reconstruction
1 code implementation • ECCV 2020 • Rohan Chabra, Jan Eric Lenssen, Eddy Ilg, Tanner Schmidt, Julian Straub, Steven Lovegrove, Richard Newcombe
Efficiently reconstructing complex and intricate surfaces at scale is a long-standing goal in machine perception.
FroDO: From Detections to 3D Objects
no code implementations • 11 May 2020 • Kejie Li, Martin Rünz, Meng Tang, Lingni Ma, Chen Kong, Tanner Schmidt, Ian Reid, Lourdes Agapito, Julian Straub, Steven Lovegrove, Richard Newcombe
We introduce FroDO, a method for accurate 3D reconstruction of object instances from RGB video that infers object location, pose and shape in a coarse-to-fine manner.
ODAM: Object Detection, Association, and Mapping using Posed RGB Video
1 code implementation • ICCV 2021 • Kejie Li, Daniel DeTone, Steven Chen, Minh Vo, Ian Reid, Hamid Rezatofighi, Chris Sweeney, Julian Straub, Richard Newcombe
Localizing objects and estimating their extent in 3D is an important step towards high-level 3D scene understanding, which has many applications in Augmented Reality and Robotics.
Nerfels: Renderable Neural Codes for Improved Camera Pose Estimation
no code implementations • 4 Jun 2022 • Gil Avraham, Julian Straub, Tianwei Shen, Tsun-Yi Yang, Hugo Germain, Chris Sweeney, Vasileios Balntas, David Novotny, Daniel DeTone, Richard Newcombe
This paper presents a framework that combines traditional keypoint-based camera pose optimization with an invertible neural rendering mechanism.
Omni3D: A Large Benchmark and Model for 3D Object Detection in the Wild
1 code implementation • CVPR 2023 • Garrick Brazil, Abhinav Kumar, Julian Straub, Nikhila Ravi, Justin Johnson, Georgia Gkioxari
In 3D, existing benchmarks are small in size and approaches specialize in few object categories and specific domains, e. g. urban driving scenes.
 3D Object Detection
3D Object Detection
 3D Object Detection From Monocular Images
+2
3D Object Detection From Monocular Images
+2
OrienterNet: Visual Localization in 2D Public Maps with Neural Matching
no code implementations • CVPR 2023 • Paul-Edouard Sarlin, Daniel DeTone, Tsun-Yi Yang, Armen Avetisyan, Julian Straub, Tomasz Malisiewicz, Samuel Rota Bulo, Richard Newcombe, Peter Kontschieder, Vasileios Balntas
We bridge this gap by introducing OrienterNet, the first deep neural network that can localize an image with sub-meter accuracy using the same 2D semantic maps that humans use.
Project Aria: A New Tool for Egocentric Multi-Modal AI Research
no code implementations • 24 Aug 2023 • Jakob Engel, Kiran Somasundaram, Michael Goesele, Albert Sun, Alexander Gamino, Andrew Turner, Arjang Talattof, Arnie Yuan, Bilal Souti, Brighid Meredith, Cheng Peng, Chris Sweeney, Cole Wilson, Dan Barnes, Daniel DeTone, David Caruso, Derek Valleroy, Dinesh Ginjupalli, Duncan Frost, Edward Miller, Elias Mueggler, Evgeniy Oleinik, Fan Zhang, Guruprasad Somasundaram, Gustavo Solaira, Harry Lanaras, Henry Howard-Jenkins, Huixuan Tang, Hyo Jin Kim, Jaime Rivera, Ji Luo, Jing Dong, Julian Straub, Kevin Bailey, Kevin Eckenhoff, Lingni Ma, Luis Pesqueira, Mark Schwesinger, Maurizio Monge, Nan Yang, Nick Charron, Nikhil Raina, Omkar Parkhi, Peter Borschowa, Pierre Moulon, Prince Gupta, Raul Mur-Artal, Robbie Pennington, Sachin Kulkarni, Sagar Miglani, Santosh Gondi, Saransh Solanki, Sean Diener, Shangyi Cheng, Simon Green, Steve Saarinen, Suvam Patra, Tassos Mourikis, Thomas Whelan, Tripti Singh, Vasileios Balntas, Vijay Baiyya, Wilson Dreewes, Xiaqing Pan, Yang Lou, Yipu Zhao, Yusuf Mansour, Yuyang Zou, Zhaoyang Lv, Zijian Wang, Mingfei Yan, Carl Ren, Renzo De Nardi, Richard Newcombe
Egocentric, multi-modal data as available on future augmented reality (AR) devices provides unique challenges and opportunities for machine perception.
Pixel-Aligned Recurrent Queries for Multi-View 3D Object Detection
no code implementations • ICCV 2023 • Yiming Xie, Huaizu Jiang, Georgia Gkioxari, Julian Straub
We present PARQ - a multi-view 3D object detector with transformer and pixel-aligned recurrent queries.
EgoLifter: Open-world 3D Segmentation for Egocentric Perception
no code implementations • 26 Mar 2024 • Qiao Gu, Zhaoyang Lv, Duncan Frost, Simon Green, Julian Straub, Chris Sweeney
In this paper we present EgoLifter, a novel system that can automatically segment scenes captured from egocentric sensors into a complete decomposition of individual 3D objects.