Search Results for author: Shengchuan Zhang
Found 21 papers, 16 papers with code
Face Sketch Synthesis Style Similarity:A New Structure Co-occurrence Texture Measure
1 code implementation • 9 Apr 2018 • Deng-Ping Fan, Shengchuan Zhang, Yu-Huan Wu, Ming-Ming Cheng, Bo Ren, Rongrong Ji, Paul L. Rosin
However, human perception of the similarity of two sketches will consider both structure and texture as essential factors and is not sensitive to slight ("pixel-level") mismatches.
CerfGAN: A Compact, Effective, Robust, and Fast Model for Unsupervised Multi-Domain Image-to-Image Translation
no code implementations • 28 May 2018 • Xiao Liu, Shengchuan Zhang, Hong Liu, Xin Liu, Cheng Deng, Rongrong Ji
In principle, CerfGAN contains a novel component, i. e., a multi-class discriminator (MCD), which gives the model an extremely powerful ability to match multiple translation mappings.
Generative Adversarial Learning Towards Fast Weakly Supervised Detection
no code implementations • CVPR 2018 • Yunhan Shen, Rongrong Ji, Shengchuan Zhang, WangMeng Zuo, Yan Wang
Without the need of annotating bounding boxes, the existing methods usually follow a two/multi-stage pipeline with an online compulsive stage to extract object proposals, which is an order of magnitude slower than fast fully supervised object detectors such as SSD [31] and YOLO [34].
Towards Visual Feature Translation
1 code implementation • CVPR 2019 • Jie Hu, Rongrong Ji, Hong Liu, Shengchuan Zhang, Cheng Deng, Qi Tian
In this paper, we make the first attempt towards visual feature translation to break through the barrier of using features across different visual search systems.
Attribute Guided Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation with Semi-supervised Learning
1 code implementation • 29 Apr 2019 • Xinyang Li, Jie Hu, Shengchuan Zhang, Xiaopeng Hong, Qixiang Ye, Chenglin Wu, Rongrong Ji
Especially, AGUIT benefits from two-fold: (1) It adopts a novel semi-supervised learning process by translating attributes of labeled data to unlabeled data, and then reconstructing the unlabeled data by a cycle consistency operation.
Information Competing Process for Learning Diversified Representations
1 code implementation • NeurIPS 2019 • Jie Hu, Rongrong Ji, Shengchuan Zhang, Xiaoshuai Sun, Qixiang Ye, Chia-Wen Lin, Qi Tian
Learning representations with diversified information remains as an open problem.
Scoot: A Perceptual Metric for Facial Sketches
1 code implementation • ICCV 2019 • Deng-Ping Fan, Shengchuan Zhang, Yu-Huan Wu, Yun Liu, Ming-Ming Cheng, Bo Ren, Paul L. Rosin, Rongrong Ji
In this paper, we design a perceptual metric, called Structure Co-Occurrence Texture (Scoot), which simultaneously considers the block-level spatial structure and co-occurrence texture statistics.
Architecture Disentanglement for Deep Neural Networks
1 code implementation • ICCV 2021 • Jie Hu, Liujuan Cao, Qixiang Ye, Tong Tong, Shengchuan Zhang, Ke Li, Feiyue Huang, Rongrong Ji, Ling Shao
Based on the experimental results, we present three new findings that provide fresh insights into the inner logic of DNNs.
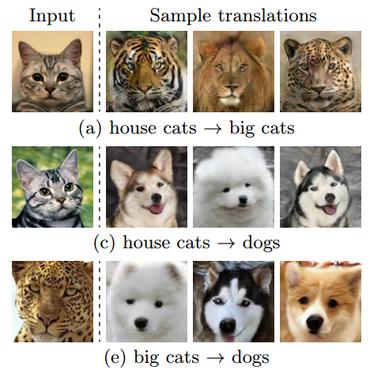
Image-to-image Translation via Hierarchical Style Disentanglement
1 code implementation • CVPR 2021 • Xinyang Li, Shengchuan Zhang, Jie Hu, Liujuan Cao, Xiaopeng Hong, Xudong Mao, Feiyue Huang, Yongjian Wu, Rongrong Ji
Recently, image-to-image translation has made significant progress in achieving both multi-label (\ie, translation conditioned on different labels) and multi-style (\ie, generation with diverse styles) tasks.
 Disentanglement
Disentanglement
 Multimodal Unsupervised Image-To-Image Translation
+1
Multimodal Unsupervised Image-To-Image Translation
+1
ISTR: End-to-End Instance Segmentation with Transformers
1 code implementation • 3 May 2021 • Jie Hu, Liujuan Cao, Yao Lu, Shengchuan Zhang, Yan Wang, Ke Li, Feiyue Huang, Ling Shao, Rongrong Ji
However, such an upgrade is not applicable to instance segmentation, due to its significantly higher output dimensions compared to object detection.
 Ranked #21 on
Instance Segmentation
on COCO test-dev
Ranked #21 on
Instance Segmentation
on COCO test-dev
Privacy-Preserving Face Recognition with Learnable Privacy Budgets in Frequency Domain
1 code implementation • 15 Jul 2022 • Jiazhen Ji, Huan Wang, Yuge Huang, Jiaxiang Wu, Xingkun Xu, Shouhong Ding, Shengchuan Zhang, Liujuan Cao, Rongrong Ji
This paper proposes a privacy-preserving face recognition method using differential privacy in the frequency domain.
Automatic Network Pruning via Hilbert-Schmidt Independence Criterion Lasso under Information Bottleneck Principle
1 code implementation • ICCV 2023 • Song Guo, Lei Zhang, Xiawu Zheng, Yan Wang, Yuchao Li, Fei Chao, Chenglin Wu, Shengchuan Zhang, Rongrong Ji
In this paper, we try to solve this problem by introducing a principled and unified framework based on Information Bottleneck (IB) theory, which further guides us to an automatic pruning approach.
Category-aware Allocation Transformer for Weakly Supervised Object Localization
no code implementations • ICCV 2023 • Zhiwei Chen, Jinren Ding, Liujuan Cao, Yunhang Shen, Shengchuan Zhang, Guannan Jiang, Rongrong Ji
Weakly supervised object localization (WSOL) aims to localize objects based on only image-level labels as supervision.
DistilPose: Tokenized Pose Regression with Heatmap Distillation
1 code implementation • CVPR 2023 • Suhang Ye, Yingyi Zhang, Jie Hu, Liujuan Cao, Shengchuan Zhang, Lei Shen, Jun Wang, Shouhong Ding, Rongrong Ji
Specifically, DistilPose maximizes the transfer of knowledge from the teacher model (heatmap-based) to the student model (regression-based) through Token-distilling Encoder (TDE) and Simulated Heatmaps.
You Only Segment Once: Towards Real-Time Panoptic Segmentation
2 code implementations • CVPR 2023 • Jie Hu, Linyan Huang, Tianhe Ren, Shengchuan Zhang, Rongrong Ji, Liujuan Cao
To reduce the computational overhead, we design a feature pyramid aggregator for the feature map extraction, and a separable dynamic decoder for the panoptic kernel generation.
Geometric-aware Pretraining for Vision-centric 3D Object Detection
1 code implementation • 6 Apr 2023 • Linyan Huang, Huijie Wang, Jia Zeng, Shengchuan Zhang, Liujuan Cao, Junchi Yan, Hongyang Li
We also conduct experiments on various image backbones and view transformations to validate the efficacy of our approach.
InterFormer: Real-time Interactive Image Segmentation
1 code implementation • ICCV 2023 • You Huang, Hao Yang, Ke Sun, Shengchuan Zhang, Liujuan Cao, Guannan Jiang, Rongrong Ji
Interactive image segmentation enables annotators to efficiently perform pixel-level annotation for segmentation tasks.
Pseudo-label Alignment for Semi-supervised Instance Segmentation
1 code implementation • ICCV 2023 • Jie Hu, Chen Chen, Liujuan Cao, Shengchuan Zhang, Annan Shu, Guannan Jiang, Rongrong Ji
Through extensive experiments conducted on the COCO and Cityscapes datasets, we demonstrate that PAIS is a promising framework for semi-supervised instance segmentation, particularly in cases where labeled data is severely limited.
Feature Denoising Diffusion Model for Blind Image Quality Assessment
no code implementations • 22 Jan 2024 • Xudong Li, Jingyuan Zheng, Runze Hu, Yan Zhang, Ke Li, Yunhang Shen, Xiawu Zheng, Yutao Liu, Shengchuan Zhang, Pingyang Dai, Rongrong Ji
Blind Image Quality Assessment (BIQA) aims to evaluate image quality in line with human perception, without reference benchmarks.
EBFT: Effective and Block-Wise Fine-Tuning for Sparse LLMs
1 code implementation • 19 Feb 2024 • Song Guo, Fan Wu, Lei Zhang, Xiawu Zheng, Shengchuan Zhang, Fei Chao, Yiyu Shi, Rongrong Ji
For instance, on the Wikitext2 dataset with LlamaV1-7B at 70% sparsity, our proposed EBFT achieves a perplexity of 16. 88, surpassing the state-of-the-art DSnoT with a perplexity of 75. 14.
DMAD: Dual Memory Bank for Real-World Anomaly Detection
no code implementations • 19 Mar 2024 • Jianlong Hu, Xu Chen, Zhenye Gan, Jinlong Peng, Shengchuan Zhang, Jiangning Zhang, Yabiao Wang, Chengjie Wang, Liujuan Cao, Rongrong Ji
To address the challenge of real-world anomaly detection, we propose a new framework named Dual Memory bank enhanced representation learning for Anomaly Detection (DMAD).












