Search Results for author: Valery Naranjo
Found 24 papers, 7 papers with code
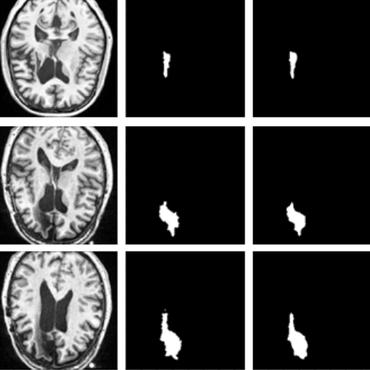
Constrained unsupervised anomaly segmentation
1 code implementation • 3 Mar 2022 • Julio Silva-Rodríguez, Valery Naranjo, Jose Dolz
In particular, the equality constraint on the attention maps in prior work is replaced by an inequality constraint, which allows more flexibility.
Looking at the whole picture: constrained unsupervised anomaly segmentation
1 code implementation • 1 Sep 2021 • Julio Silva-Rodríguez, Valery Naranjo, Jose Dolz
In particular, the equality constraint on the attention maps in prior work is replaced by an inequality constraint, which allows more flexibility.
Attention to detail: inter-resolution knowledge distillation
2 code implementations • 11 Jan 2024 • Rocío del Amor, Julio Silva-Rodríguez, Adrián Colomer, Valery Naranjo
The development of computer vision solutions for gigapixel images in digital pathology is hampered by significant computational limitations due to the large size of whole slide images.
Going Deeper through the Gleason Scoring Scale: An Automatic end-to-end System for Histology Prostate Grading and Cribriform Pattern Detection
1 code implementation • 21 May 2021 • Julio Silva-Rodríguez, Adrián Colomer, María A. Sales, Rafael Molina, Valery Naranjo
The objective of the work presented in this paper is to develop a deep-learning-based system able to support pathologists in the daily analysis of prostate biopsies.
Self-learning for weakly supervised Gleason grading of local patterns
1 code implementation • 21 May 2021 • Julio Silva-Rodríguez, Adrián Colomer, Jose Dolz, Valery Naranjo
Particularly, the proposed model brings an average improvement on the Cohen's quadratic kappa (k) score of nearly 18% compared to full-supervision for the patch-level Gleason grading task.
WeGleNet: A Weakly-Supervised Convolutional Neural Network for the Semantic Segmentation of Gleason Grades in Prostate Histology Images
1 code implementation • 21 May 2021 • Julio Silva-Rodríguez, Adrián Colomer, Valery Naranjo
Regarding the estimation of the core-level Gleason score, we obtained a k of 0. 76 and 0. 67 between the model and two different pathologists.
REFUGE Challenge: A Unified Framework for Evaluating Automated Methods for Glaucoma Assessment from Fundus Photographs
no code implementations • 8 Oct 2019 • José Ignacio Orlando, Huazhu Fu, João Barbossa Breda, Karel van Keer, Deepti. R. Bathula, Andrés Diaz-Pinto, Ruogu Fang, Pheng-Ann Heng, Jeyoung Kim, Joonho Lee, Joonseok Lee, Xiaoxiao Li, Peng Liu, Shuai Lu, Balamurali Murugesan, Valery Naranjo, Sai Samarth R. Phaye, Sharath M. Shankaranarayana, Apoorva Sikka, Jaemin Son, Anton Van Den Hengel, Shujun Wang, Junyan Wu, Zifeng Wu, Guanghui Xu, Yongli Xu, Pengshuai Yin, Fei Li, Yanwu Xu, Xiulan Zhang, Hrvoje Bogunović
As part of REFUGE, we have publicly released a data set of 1200 fundus images with ground truth segmentations and clinical glaucoma labels, currently the largest existing one.
Gleason Grading of Histology Prostate Images through Semantic Segmentation via Residual U-Net
1 code implementation • 22 May 2020 • Amartya Kalapahar, Julio Silva-Rodríguez, Adrián Colomer, Fernando López-Mir, Valery Naranjo
Worldwide, prostate cancer is one of the main cancers affecting men.
Glaucoma Detection From Raw Circumapillary OCT Images Using Fully Convolutional Neural Networks
no code implementations • 29 May 2020 • Gabriel García, Rocío del Amor, Adrián Colomer, Valery Naranjo
Nowadays, glaucoma is the leading cause of blindness worldwide.
Analysis of Hand-Crafted and Automatic-Learned Features for Glaucoma Detection Through Raw Circmpapillary OCT Images
no code implementations • 9 Sep 2020 • Gabriel García, Adrián Colomer, Valery Naranjo
Taking into account that glaucoma is the leading cause of blindness worldwide, we propose in this paper three different learning methodologies for glaucoma detection in order to elucidate that traditional machine-learning techniques could outperform deep-learning algorithms, especially when the image data set is small.
An Attention-based Weakly Supervised framework for Spitzoid Melanocytic Lesion Diagnosis in WSI
no code implementations • 20 Apr 2021 • Rocío del Amor, Laëtitia Launet, Adrián Colomer, Anaïs Moscardó, Andrés Mosquera-Zamudio, Carlos Monteagudo, Valery Naranjo
Nevertheless, no automatic CAD systems have yet been proposed for the analysis of spitzoid lesions.
Prostate Gland Segmentation in Histology Images via Residual and Multi-Resolution U-Net
no code implementations • 21 May 2021 • Julio Silva-Rodríguez, Elena Payá-Bosch, Gabriel García, Adrián Colomer, Valery Naranjo
Prostate cancer is one of the most prevalent cancers worldwide.
Circumpapillary OCT-Focused Hybrid Learning for Glaucoma Grading Using Tailored Prototypical Neural Networks
no code implementations • 25 Jun 2021 • Gabriel García, Rocío del Amor, Adrián Colomer, Rafael Verdú-Monedero, Juan Morales-Sánchez, Valery Naranjo
Glaucoma is one of the leading causes of blindness worldwide and Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is the quintessential imaging technique for its detection.
A Novel Self-Learning Framework for Bladder Cancer Grading Using Histopathological Images
no code implementations • 25 Jun 2021 • Gabriel García, Anna Esteve, Adrián Colomer, David Ramos, Valery Naranjo
Recently, bladder cancer has been significantly increased in terms of incidence and mortality.
A self-training framework for glaucoma grading in OCT B-scans
no code implementations • 23 Nov 2021 • Gabriel García, Adrián Colomer, Rafael Verdú-Monedero, José Dolz, Valery Naranjo
Particularly, the proposed two-step learning methodology resorts to pseudo-labels generated during the first step to augment the training dataset on the target domain, which is then used to train the final target model.
DCASE 2022: Comparative Analysis Of CNNs For Acoustic Scene Classification Under Low-Complexity Considerations
no code implementations • 16 Jun 2022 • Josep Zaragoza-Paredes, Javier Naranjo-Alcazar, Valery Naranjo, Pedro Zuccarello
Due to the drift in this field of study, this task has two limitations in terms of model complexity.
Challenging mitosis detection algorithms: Global labels allow centroid localization
no code implementations • 30 Nov 2022 • Claudio Fernandez-Martín, Umay Kiraz, Julio Silva-Rodríguez, Sandra Morales, Emiel Janssen, Valery Naranjo
Mitotic activity is a crucial proliferation biomarker for the diagnosis and prognosis of different types of cancers.
Self-supervised learning of a tailored Convolutional Auto Encoder for histopathological prostate grading
no code implementations • 21 Mar 2023 • Zahra Tabatabaei, Adrian colomer, Kjersti Engan, Javier Oliver, Valery Naranjo
In particular, a tailored Convolutional Auto Encoder (CAE) is trained to reconstruct 128x128x3 patches of prostate cancer Whole Slide Images (WSIs) as a pretext task.
WWFedCBMIR: World-Wide Federated Content-Based Medical Image Retrieval
no code implementations • 5 May 2023 • Zahra Tabatabaei, Yuandou Wang, Adrián Colomer, Javier Oliver Moll, Zhiming Zhao, Valery Naranjo
The study shows that the FedCBMIR method increases the F1-Score (F1S) of each client to 98%, 96%, 94%, and 97% in the BreaKHis experiment with a generalized model of four magnifications and does so in 6. 30 hours less time than total local training.
Towards More Transparent and Accurate Cancer Diagnosis with an Unsupervised CAE Approach
no code implementations • 19 May 2023 • Zahra Tabatabaei, Adrian colomer, Javier Oliver Moll, Valery Naranjo
UCBMIR outperformed previous studies, achieving a top 5 recall of 99% and 80% on BreaKHis and SICAPv2, respectively, using the first evaluation technique.
HistoColAi: An Open-Source Web Platform for Collaborative Digital Histology Image Annotation with AI-Driven Predictive Integration
no code implementations • 11 Jul 2023 • Cristian Camilo Pulgarín-Ospina, Rocío del Amor, Adrián Colomera, Julio Silva-Rodríguez, Valery Naranjo
Digital pathology has become a standard in the pathology workflow due to its many benefits.
Siamese Content-based Search Engine for a More Transparent Skin and Breast Cancer Diagnosis through Histological Imaging
no code implementations • 16 Jan 2024 • Zahra Tabatabaei, Adrián Colomer, Javier Oliver Moll, Valery Naranjo
The Breast-twins model achieves 70% of the F1score at the top first, which exceeds the other state-of-the-art methods at a higher amount of K such as 5 and 400.
Emotional Voice Messages (EMOVOME) database: emotion recognition in spontaneous voice messages
no code implementations • 27 Feb 2024 • Lucía Gómez Zaragozá, Rocío del Amor, Elena Parra Vargas, Valery Naranjo, Mariano Alcañiz Raya, Javier Marín-Morales
For speech, we used the standard eGeMAPS feature set and support vector machines, obtaining 49. 27% and 44. 71% unweighted accuracy for valence and arousal respectively.
Speech emotion recognition from voice messages recorded in the wild
no code implementations • 4 Mar 2024 • Lucía Gómez-Zaragozá, Óscar Valls, Rocío del Amor, María José Castro-Bleda, Valery Naranjo, Mariano Alcañiz Raya, Javier Marín-Morales
The pre-trained Unispeech-L model and its combination with eGeMAPS achieved the highest results, with 61. 64% and 55. 57% Unweighted Accuracy (UA) for 3-class valence and arousal prediction respectively, a 10% improvement over baseline models.