Sleep Quality
9 papers with code • 1 benchmarks • 0 datasets
( Image credit: DeepSleep )
Subtasks
Most implemented papers
DOSED: a deep learning approach to detect multiple sleep micro-events in EEG signal
The proposed approach, applied here on sleep related micro-architecture events, is inspired by object detectors developed for computer vision such as YOLO and SSD.
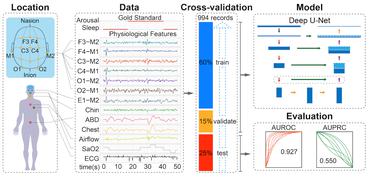
Deepsleep: Fast and Accurate Delineation of Sleep Arousals at Millisecond Resolution by Deep Learning
Background: Sleep arousals are transient periods of wakefulness punctuated into sleep.
An Attention-Based Deep Learning Approach for Sleep Stage Classification With Single-Channel EEG
The MRCNN can extract low and high frequency features and the AFR is able to improve the quality of the extracted features by modeling the inter-dependencies between the features.
Quantified Sleep: Machine learning techniques for observational n-of-1 studies
This paper applies statistical learning techniques to an observational Quantified-Self (QS) study to build a descriptive model of sleep quality.
MAUS: A Dataset for Mental Workload Assessmenton N-back Task Using Wearable Sensor
Besides, we also presents a reproducible baseline system as a preliminary benchmark (The code of the baseline system on MAUS dataset is available on Github: https://github. com/rickwu11/MAUS\_dataset\_baseline\_system), which testing accuracy are 71. 6 %, 66. 7 %, and 59. 9 % in ECG, fingertip PPG, wristband PPG, respectively.
Advanced sleep spindle identification with neural networks
Our model's performance exceeds that of the state-of-the-art detector and of most experts in the MODA dataset.
DeepSleep 2.0: Automated Sleep Arousal Segmentation via Deep Learning
DeepSleep 2. 0 is a compact version of DeepSleep, a state-of-the-art, U-Net-inspired, fully convolutional deep neural network, which achieved the highest unofficial score in the 2018 PhysioNet Computing Challenge.
A Knowledge Distillation Framework For Enhancing Ear-EEG Based Sleep Staging With Scalp-EEG Data
Sleep plays a crucial role in the well-being of human lives.
ZzzGPT: An Interactive GPT Approach to Enhance Sleep Quality
In today's world, sleep quality is pivotal for overall well-being.