Adversarial Attacks on Knowledge Graph Embeddings via Instance Attribution Methods
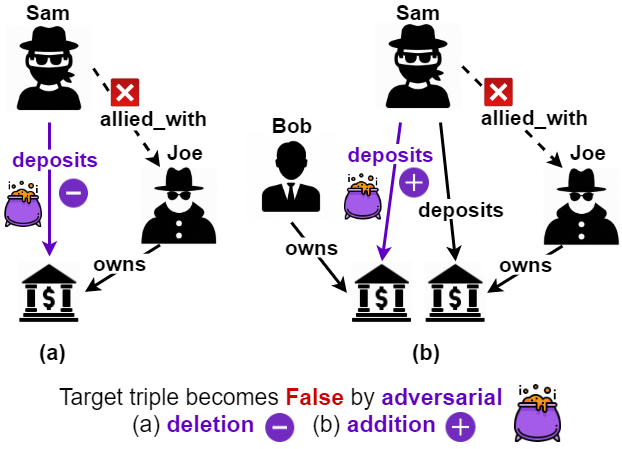
Despite the widespread use of Knowledge Graph Embeddings (KGE), little is known about the security vulnerabilities that might disrupt their intended behaviour. We study data poisoning attacks against KGE models for link prediction. These attacks craft adversarial additions or deletions at training time to cause model failure at test time. To select adversarial deletions, we propose to use the model-agnostic instance attribution methods from Interpretable Machine Learning, which identify the training instances that are most influential to a neural model's predictions on test instances. We use these influential triples as adversarial deletions. We further propose a heuristic method to replace one of the two entities in each influential triple to generate adversarial additions. Our experiments show that the proposed strategies outperform the state-of-art data poisoning attacks on KGE models and improve the MRR degradation due to the attacks by up to 62% over the baselines.
PDF Abstract EMNLP 2021 PDF EMNLP 2021 Abstract