A Deep Learning Approach to Block-based Compressed Sensing of Images
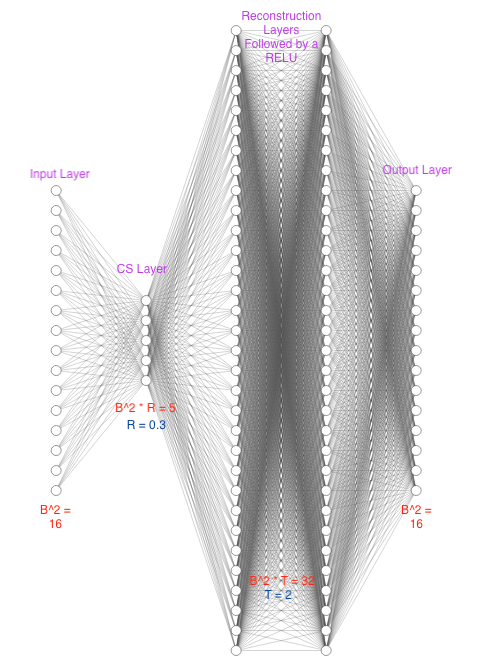
Compressed sensing (CS) is a signal processing framework for efficiently reconstructing a signal from a small number of measurements, obtained by linear projections of the signal. Block-based CS is a lightweight CS approach that is mostly suitable for processing very high-dimensional images and videos: it operates on local patches, employs a low-complexity reconstruction operator and requires significantly less memory to store the sensing matrix. In this paper we present a deep learning approach for block-based CS, in which a fully-connected network performs both the block-based linear sensing and non-linear reconstruction stages. During the training phase, the sensing matrix and the non-linear reconstruction operator are \emph{jointly} optimized, and the proposed approach outperforms state-of-the-art both in terms of reconstruction quality and computation time. For example, at a 25% sensing rate the average PSNR advantage is 0.77dB and computation time is over 200-times faster.
PDF Abstract