Model-Based Reinforcement Learning with Adversarial Training for Online Recommendation
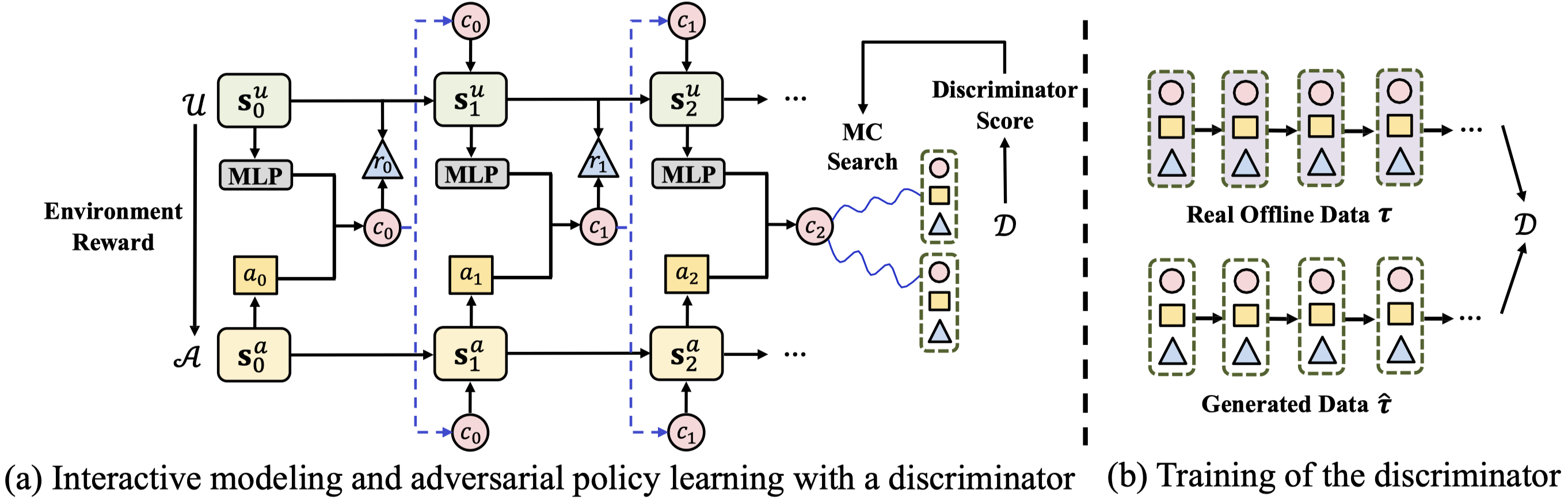
Reinforcement learning is well suited for optimizing policies of recommender systems. Current solutions mostly focus on model-free approaches, which require frequent interactions with the real environment, and thus are expensive in model learning. Offline evaluation methods, such as importance sampling, can alleviate such limitations, but usually request a large amount of logged data and do not work well when the action space is large. In this work, we propose a model-based reinforcement learning solution which models user-agent interaction for offline policy learning via a generative adversarial network. To reduce bias in the learned model and policy, we use a discriminator to evaluate the quality of generated data and scale the generated rewards. Our theoretical analysis and empirical evaluations demonstrate the effectiveness of our solution in learning policies from the offline and generated data.
PDF Abstract