A Scalable and Generalizable Pathloss Map Prediction
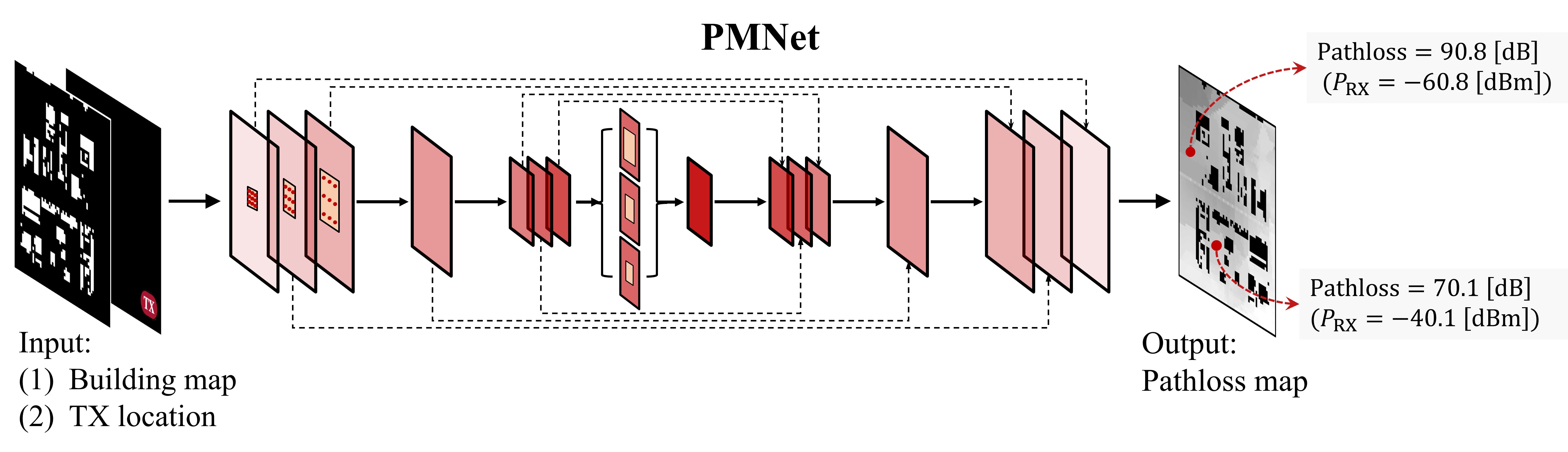
Large-scale channel prediction, i.e., estimation of the pathloss from geographical/morphological/building maps, is an essential component of wireless network planning. Ray tracing (RT)-based methods have been widely used for many years, but they require significant computational effort that may become prohibitive with the increased network densification and/or use of higher frequencies in B5G/6G systems. In this paper, we propose a data-driven, model-free pathloss map prediction (PMP) method, called PMNet. PMNet uses a supervised learning approach: it is trained on a limited amount of RT (or channel measurement) data and map data. Once trained, PMNet can predict pathloss over location with high accuracy (an RMSE level of $10^{-2}$) in a few milliseconds. We further extend PMNet by employing transfer learning (TL). TL allows PMNet to learn a new network scenario quickly (x5.6 faster training) and efficiently (using x4.5 less data) by transferring knowledge from a pre-trained model, while retaining accuracy. Our results demonstrate that PMNet is a scalable and generalizable ML-based PMP method, showing its potential to be used in several network optimization applications.
PDF Abstract