AdaDGS: An adaptive black-box optimization method with a nonlocal directional Gaussian smoothing gradient
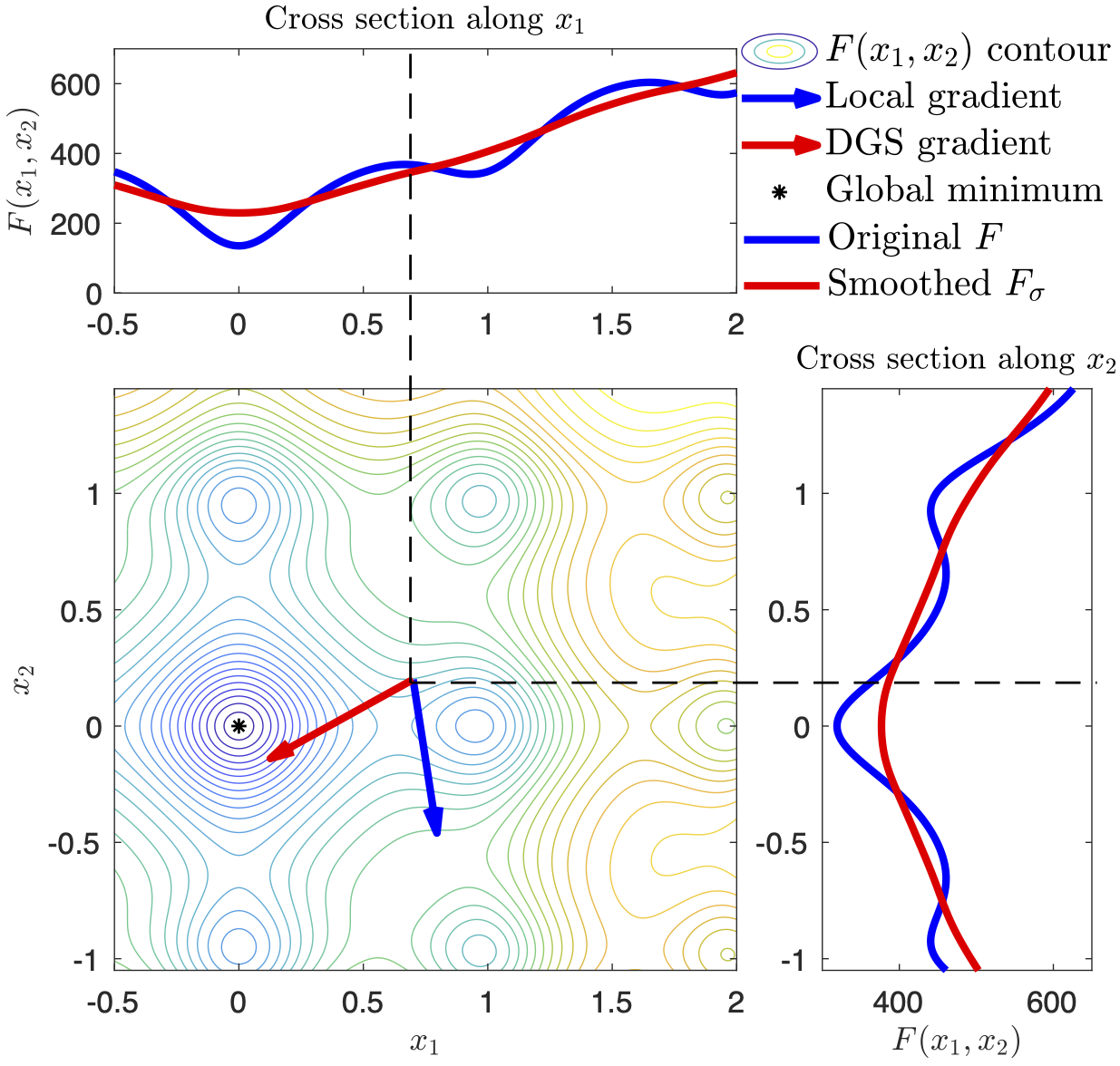
The local gradient points to the direction of the steepest slope in an infinitesimal neighborhood. An optimizer guided by the local gradient is often trapped in local optima when the loss landscape is multi-modal. A directional Gaussian smoothing (DGS) approach was recently proposed in (Zhang et al., 2020) and used to define a truly nonlocal gradient, referred to as the DGS gradient, for high-dimensional black-box optimization. Promising results show that replacing the traditional local gradient with the DGS gradient can significantly improve the performance of gradient-based methods in optimizing highly multi-modal loss functions. However, the optimal performance of the DGS gradient may rely on fine tuning of two important hyper-parameters, i.e., the smoothing radius and the learning rate. In this paper, we present a simple, yet ingenious and efficient adaptive approach for optimization with the DGS gradient, which removes the need of hyper-parameter fine tuning. Since the DGS gradient generally points to a good search direction, we perform a line search along the DGS direction to determine the step size at each iteration. The learned step size in turn will inform us of the scale of function landscape in the surrounding area, based on which we adjust the smoothing radius accordingly for the next iteration. We present experimental results on high-dimensional benchmark functions, an airfoil design problem and a game content generation problem. The AdaDGS method has shown superior performance over several the state-of-the-art black-box optimization methods.
PDF Abstract