AutoTimes: Autoregressive Time Series Forecasters via Large Language Models
Foundation models of time series have not been fully developed due to the limited availability of large-scale time series and the underexploration of scalable pre-training. Based on the similar sequential structure of time series and natural language, increasing research demonstrates the feasibility of leveraging large language models (LLM) for time series. Nevertheless, prior methods may overlook the consistency in aligning time series and natural language, resulting in insufficient utilization of the LLM potentials. To fully exploit the general-purpose token transitions learned from language modeling, we propose AutoTimes to repurpose LLMs as Autoregressive Time series forecasters, which is consistent with the acquisition and utilization of LLMs without updating the parameters. The consequent forecasters can handle flexible series lengths and achieve competitive performance as prevalent models. Further, we present token-wise prompting that utilizes corresponding timestamps to make our method applicable to multimodal scenarios. Analysis demonstrates our forecasters inherit zero-shot and in-context learning capabilities of LLMs. Empirically, AutoTimes exhibits notable method generality and achieves enhanced performance by basing on larger LLMs, additional texts, or time series as instructions.
PDF Abstract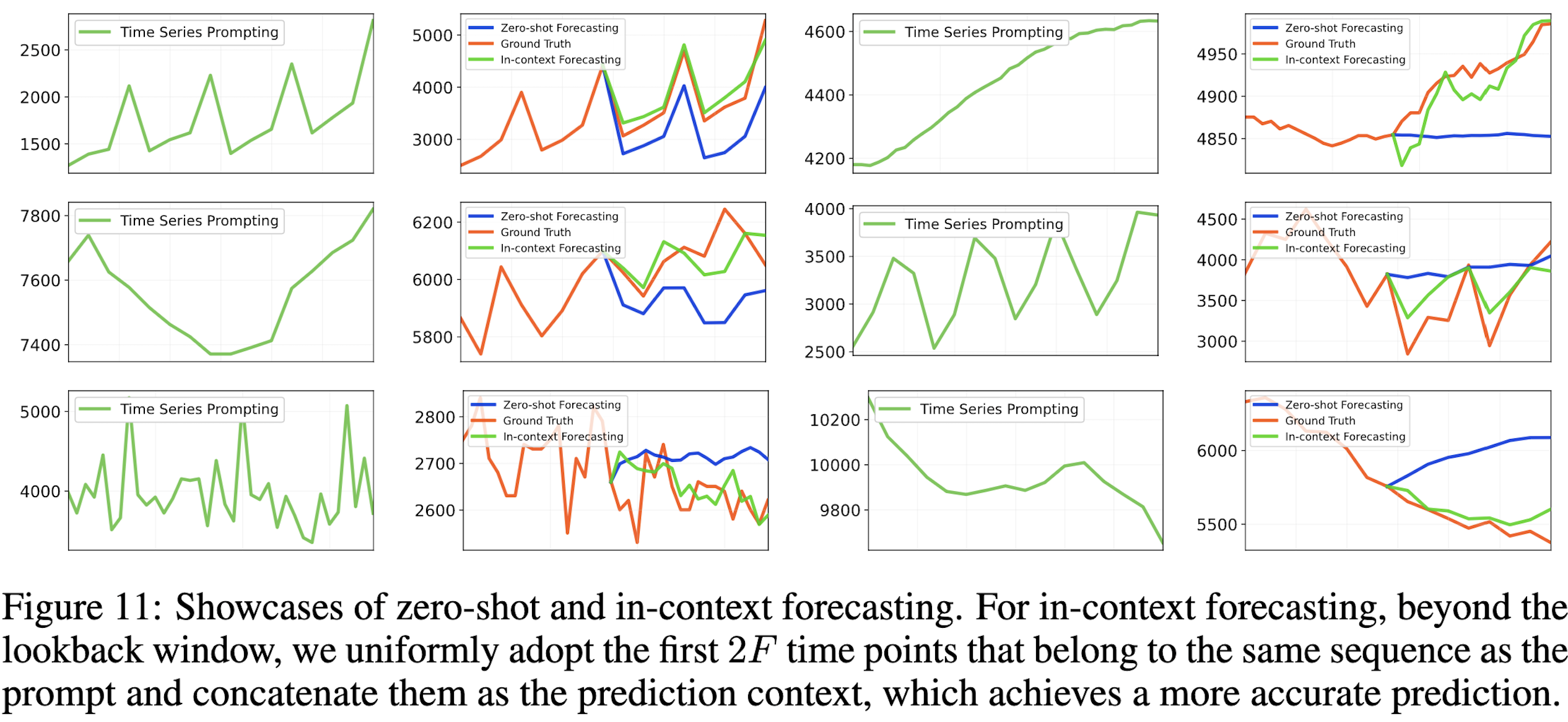



 ETT
ETT