Distributed speech separation in spatially unconstrained microphone arrays
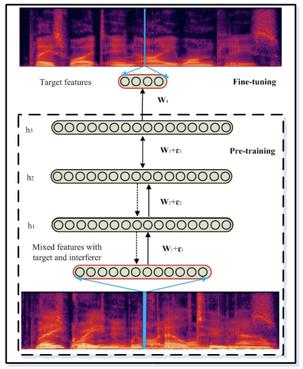
Speech separation with several speakers is a challenging task because of the non-stationarity of the speech and the strong signal similarity between interferent sources. Current state-of-the-art solutions can separate well the different sources using sophisticated deep neural networks which are very tedious to train. When several microphones are available, spatial information can be exploited to design much simpler algorithms to discriminate speakers. We propose a distributed algorithm that can process spatial information in a spatially unconstrained microphone array. The algorithm relies on a convolutional recurrent neural network that can exploit the signal diversity from the distributed nodes. In a typical case of a meeting room, this algorithm can capture an estimate of each source in a first step and propagate it over the microphone array in order to increase the separation performance in a second step. We show that this approach performs even better when the number of sources and nodes increases. We also study the influence of a mismatch in the number of sources between the training and testing conditions.
PDF Abstract